Clinical Significance of PIK3CA and ESR1 Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA: Analysis from the MONARCH 2 Study of Abemaciclib plus Fulvestrant
- PMID: 35121623
- PMCID: PMC10234145
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-3276
Clinical Significance of PIK3CA and ESR1 Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA: Analysis from the MONARCH 2 Study of Abemaciclib plus Fulvestrant
Erratum in
-
Correction: Clinical Significance of PIK3CA and ESR1 Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA: Analysis from the MONARCH 2 Study of Abemaciclib plus Fulvestrant.Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 14;28(20):4587. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2874. Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36239018 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: PIK3CA and ESR1 mutations have been implicated in resistance to endocrine therapy (ET) in HR+, HER2- advanced breast cancer (ABC). Inhibition of CDK4 and 6 has been hypothesized as a therapeutic strategy to overcome endocrine resistance in patients with PIK3CA- or ESR1-mutant breast cancers. The objective of this exploratory analysis was to assess efficacy of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant in patients with or without PIK3CA or ESR1 mutations in MONARCH 2.
Patients and methods: MONARCH 2 was a global, randomized, double-blind phase III trial of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant in 669 women with HR+, HER2- ABC, which had progressed on ET. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive abemaciclib plus fulvestrant or placebo plus fulvestrant. Exploratory analyses assessed progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), and other endpoints, in patients with or without PIK3CA or ESR1 mutations detectable in baseline ctDNA.
Results: From the MONARCH 2 population, 219 and 248 patient samples were successfully analyzed for either PIK3CA or ESR1 mutations, respectively. Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant improved PFS compared with placebo plus fulvestrant in both PIK3CA-wild-type (median 16.9 months vs. 12.3 months; HR, 0.51; 95% CI, 0.33-0.78) and PIK3CA-mutant subgroups (median 17.1 months vs. 5.7 months; HR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.33-0.84), as well as both ESR1-wild-type (median 15.3 months vs. 11.2 months; HR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.27-0.71) and ESR1-mutant subgroups (median 20.7 months vs. 13.1 months; HR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.37-0.79). Additional endpoints, including OS, were also improved following treatment with abemaciclib plus fulvestrant regardless of PIK3CA or ESR1 mutation status.
Conclusions: Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant was effective regardless of PIK3CA or ESR1 mutation status, with benefit in both PFS and OS, with a numerically greater improvement in median PFS relative to placebo plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA- or ESR1-mutant tumors compared with the respective wild-type subgroups, in women with HR+, HER2- ABC that had progressed on ET.
©2022 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
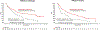
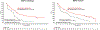
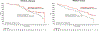
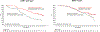
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J, Inoue K, Pivot X, et al. MONARCH 2: abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol 2017;35:2875–84. - PubMed
-
- Araki K, Miyoshi Y. Mechanism of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: the important role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR in estrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2018;25:392–401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

