Targeting PUS7 suppresses tRNA pseudouridylation and glioblastoma tumorigenesis
- PMID: 35121864
- PMCID: PMC8809511
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-021-00238-0
Targeting PUS7 suppresses tRNA pseudouridylation and glioblastoma tumorigenesis
Abstract
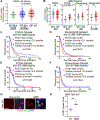
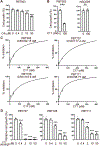
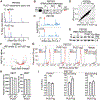
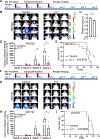
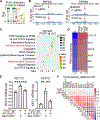
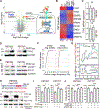
Pseudouridine is the most frequent epitranscriptomic modification. However, its cellular functions remain largely unknown. Here, we show that pseudouridine synthase 7 (PUS7) is highly expressed in glioblastoma versus normal brain tissues, and high PUS7 expression levels are associated with worse survival in patients with glioblastoma. PUS7 expression and catalytic activity are required for glioblastoma stem cell (GSC) tumorigenesis. Mechanistically, we identify PUS7 targets in GSCs through small RNA pseudouridine sequencing and show that pseudouridylation of PUS7-regulated transfer RNA is critical for codon-specific translational control of key regulators of GSCs. Moreover, we identify chemical inhibitors for PUS7 and show that these compounds prevent PUS7-mediated pseudouridine modification, suppress tumorigenesis and extend the life span of tumor-bearing mice. Overall, we identify an epitranscriptomic regulatory mechanism in glioblastoma and provide preclinical evidence of a potential therapeutic strategy for glioblastoma.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
C. H is a scientific founder and a member of the scientific advisory board of Accent Therapeutics Inc. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

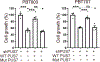




Comment in
-
A therapy PUSh for GBM.Nat Cancer. 2021 Sep;2(9):876-878. doi: 10.1038/s43018-021-00255-z. Nat Cancer. 2021. PMID: 35121866 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

