Targeting PAK4 to reprogram the vascular microenvironment and improve CAR-T immunotherapy for glioblastoma
- PMID: 35121889
- PMCID: PMC10097424
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-020-00147-8
Targeting PAK4 to reprogram the vascular microenvironment and improve CAR-T immunotherapy for glioblastoma
Abstract
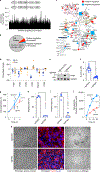
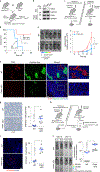
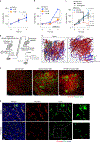
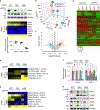
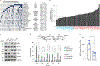
Malignant solid tumors are characterized by aberrant vascularity that fuels the formation of an immune-hostile microenvironment and induces resistance to immunotherapy. Vascular abnormalities may be driven by pro-angiogenic pathway activation and genetic reprogramming in tumor endothelial cells (ECs). Here, our kinome-wide screening of mesenchymal-like transcriptional activation in human glioblastoma (GBM)-derived ECs identifies p21-activated kinase 4 (PAK4) as a selective regulator of genetic reprogramming and aberrant vascularization. PAK4 knockout induces adhesion protein re-expression in ECs, reduces vascular abnormalities, improves T cell infiltration and inhibits GBM growth in mice. Moreover, PAK4 inhibition normalizes the tumor vascular microenvironment and sensitizes GBM to chimeric antigen receptor-T cell immunotherapy. Finally, we reveal a MEF2D/ZEB1- and SLUG-mediated mechanism by which PAK4 reprograms the EC transcriptome and downregulates claudin-14 and VCAM-1 expression, enhancing vessel permeability and reducing T cell adhesion to the endothelium. Thus, targeting PAK4-mediated EC plasticity may offer a unique opportunity to recondition the vascular microenvironment and strengthen cancer immunotherapy.
© 2020. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc. part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Y.F. is an inventor on a patent application covering the use of PAK4 inhibitors for vessel normalization therapy. L.Z. received research funding from AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene and Prelude Therapeutics.
Figures






References
-
- Carmeliet P & Jain RK Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 10, 417–427 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Weis SM & Cheresh DA Tumor angiogenesis: molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat. Med 17, 1359–1370 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D & Weinberg RA Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144, 646–674 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

