Rolling Reviews During COVID-19: The European Union Experience in a Global Context
- PMID: 35123802
- PMCID: PMC8743449
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2022.01.001
Rolling Reviews During COVID-19: The European Union Experience in a Global Context
Abstract
Purpose: Many regulators offered new ways of working to help combat the COVID-19 pandemic, and the rolling review procedure is an important and successful example. In rolling reviews, data are submitted and reviewed as they become available before the full data package is available. This approach is resource intensive but faster than standard review processes and therefore of benefit to society and patients during a health emergency. In this study, we analyze the European Medicines Agency (EMA) rolling review process and extract learning, based on the vaccines and treatments that have been approved to date (November 2021), and formulate 3 suggestions for the future.
Methods: Data and information on rolling reviews and similar related processes were collected from health authority websites across the globe with a focus on the EMA. Literature searches in PubMed and checking company websites for additional information were conducted to complement and corroborate findings as required.
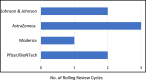
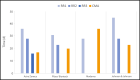
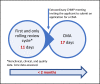
Findings: The duration of a rolling review cycle and the number of cycles before a conditional marketing authorization differ among different applications. Through the rolling review process, COVID-19 vaccines could be approved in record times, ranging from 17 to 36 days. The rolling review process is not limited to vaccines but is applied to promising treatments as well.
Implications: This study indicates that rolling reviews can be successfully conducted during a health emergency, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, to meet an unmet medical need. Other critical conditions or life-threatening diseases with unmet needs exist and may be suitable to be addressed by a rolling review process to accelerate patient access to life-changing treatments. Indeed, we call for an evaluation of the rolling review process, its use, and its efficiency to capture learning with the aim of building a new, lean, and effective expedited review procedure that could be institutionalized and added to the regulatory toolbox.
Keywords: COVID-19; dynamic regulatory assessment; expedited approval pathways; pandemic; rolling review; vaccines.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure All authors are Sanofi employees and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. All authors hold positions within the pharmaceutical industry, but they have not received any grant, honoraria, or other compensation to author this paper. The study was conceived of, executed on, and written during the authors’ daily job. The authors have indicated that they have no other conflicts of interest regarding the content of this article.
Figures

References
-
- WHO, Timeline: WHO's COVID-19 response https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/interact... Last accessed 29 October 2021
-
- Domenico Cucinotta, Maurizio Vanelli, WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32191675/ Last accessed 29 October 2021 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Winona Rei Bolislis Maria Lucia de Lucia, Felipe Dolz Runyi Mo Makoto Nagaoka Heraclio Rodriguez May Li Woon Wei Yu Thomas C. Kühler, Regulatory Agilities in the Time of COVID-19: Overview, Trends, and Opportunities https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0149291820305257 Last accessed 29 October 2021 - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO and ICMRA joint Report on the review of regulatory flexibilities/agilities as implemented by National Regulatory Authorities during Covid-19 pandemic –December 2020 https://www.icmra.info/drupal/sites/default/files/2021-12/Regulatory_Fle... Last accessed 2 December 2021
-
- Bruno Speder:“ Rolling Reviews – a useful tool to speed up the regulatory review process” https://hvivo.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Speder-Bruno-Rolling-Review... Last accessed 26 November 2021
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

