Cardiovascular risk factor progression in adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 35123868
- PMCID: PMC8903081
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.108123
Cardiovascular risk factor progression in adolescents and young adults with youth-onset type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Aims: Youth-onset type 2 diabetes (T2D) confers a high risk of early adverse cardiovascular morbidity. We describe the cumulative incidence and prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors over time and examine relationships with diabetes progression in young adults with youth-onset T2D from the Treatment Options for type 2 Diabetes in Adolescents and Youth (TODAY) study.
Methods: Longitudinal data was used to evaluate the relationships between hypertension, LDL-C dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, and smoking with risk factors in 677 participants.
Results: Baseline mean age was 14 ± 2 years and mean follow-up 10.2 ± 4.5 years. The 14-year cumulative incidence of hypertension, LDL-C dyslipidemia, and hypertriglyceridemia was 59%, 33%, and 37% respectively. Average prevalence of reported smoking was 23%. Male sex, non-Hispanic white race/ethnicity, obesity, poor glycemic control, lower insulin sensitivity, and reduced beta-cell function were significantly associated with an unfavorable risk profile. At end of follow-up, 54% had ≥2 cardiovascular risk factors in addition to T2D.
Conclusions: Cardiovascular risk factor incidence and prevalence was high over a decade of follow-up in young adults with youth-onset T2D. Glucose control and management of cardiovascular risk factors is critical in youth with T2D for prevention of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00081328 NCT01364350 NCT02310724.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Hyperlipidemia; Hypertension; Smoking; Type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

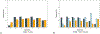
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

