Electroacupuncture and acupuncture in the treatment of anxiety - A double blinded randomized parallel clinical trial
- PMID: 35124475
- PMCID: PMC9760487
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2022.101541
Electroacupuncture and acupuncture in the treatment of anxiety - A double blinded randomized parallel clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The estimated number of people living with anxiety disorders worldwide is around 264 million and is estimated to have worsened with the recent pandemic of COVID-19. Acupuncture has shown to have excellent therapeutic effects in reducing anxiety.
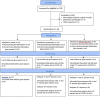
Design: Double-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial with 56 participants (21-82 years) with anxiety diagnosed by 3 different anxiety scales (BAI, GAD-7 and OASIS). A 30-min acupuncture session was applied once a week for 10 weeks.
Aims: Evaluate the effectiveness of acupuncture and electroacupuncture in the treatment of anxiety to verify if: (1) People with high anxiety report reduced scores after 5 and 10 sessions; (2) Salivary cortisol levels accompanied the reduced scores; (3) Electroacupuncture treatment is more effective than acupuncture; (4) the treatments is independent of anxiolytic medication.
Methods: Volunteers were randomized into 3 groups (control, acupuncture, and electroacupuncture). The results were analyzed by anxiety scales and salivary cortisol tests.
Results: The findings show an improvement in anxiety, assessed by BAI, GAD-7 and OASIS, after the 5th session of acupuncture (p < 0.05) and electroacupuncture (p < 0.05) and the 10th session for both techniques (p < 0.001). The salivary cortisol values measured in the morning followed this pattern (p < 0.05), although the reduction of the night cortisol values was not statistically significant. Electroacupuncture and acupuncture show similar efficacy. The positive effect after the treatments is independent of anxiolytic medication (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: Acupuncture and electroacupuncture are effective in treating anxiety on their own or as adjuncts to pharmacological therapy.
Trial registration number: NºP445-08/2017 (Unidade de Investigação em Ciências da Saúde).
Keywords: Acupuncture; Anxiety; Anxiety surveys; Electroacupuncture; Salivary cortisol.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
No.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Geneva; 2017. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates.
-
- Salari N., Hosseinian-Far A., Jalali R., Vaisi-Raygani A., Rasoulpoor S., Mohammadi M., Rasoulpoor S. Prevalence of stress, anxiety, depression among the general population during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Glob. Health. 2020;16(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caldas-de-Almeida J.M.X. Nova Medical School Lisbon; 2013. Estudo Epidemiológico Nacional de Saúde Mental – 1° Relatório (National Mental Health Epidemiological Study – 1st Report)
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

