Identification of a chromatin regulator signature and potential candidate drugs for bladder cancer
- PMID: 35125116
- PMCID: PMC8819906
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-021-00212-x
Identification of a chromatin regulator signature and potential candidate drugs for bladder cancer
Abstract
Background: Bladder cancer (BLCA) is a malignant tumor with a dismay outcome. Increasing evidence has confirmed that chromatin regulators (CRs) are involved in cancer progression. Therefore, we aimed to explore the function and prognostic value of CRs in BLCA patients.
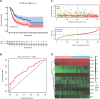
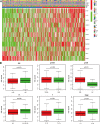
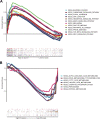
Methods: Chromatin regulators (CRs) were acquired from the previous top research. The mRNA expression and clinical information were downloaded from TCGA and GEO datasets. Cox regression analysis and least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis were performed to select the prognostic gene and construct the risk model for predicting outcome in BLCA. The Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to assess the prognosis between high- and low-risk groups. We also investigated the drug sensitivity difference between high- and low-risk groups. CMAP dataset was performed to screen the small molecule drugs for treatment.
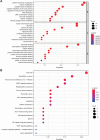
Results: We successfully constructed and validated an 11 CRs-based model for predicting the prognosis of patients with BLCA. Moreover, we also found 11 CRs-based model was an independent prognostic factor. Functional analysis suggested that CRs were mainly enriched in cancer-related signaling pathways. The CR-based model was also correlated with immune cells infiltration and immune checkpoint. Patients in the high-risk group were more sensitive to several drugs, such as mitomycin C, gemcitabine, cisplatin. Eight small molecule drugs could be beneficial to treatment for BLCA patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our study provided novel insights into the function of CRs in BLCA. We identified a reliable prognostic biomarker for the survival of patients with BLCA.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Chromatin regulators; Prognosis; TCGA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Development and validation of a novel lipid metabolism-related gene prognostic signature and candidate drugs for patients with bladder cancer.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 Oct 27;20(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01554-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34706720 Free PMC article.
-
A novel chromatin regulator-related immune checkpoint related gene prognostic signature and potential candidate drugs for endometrial cancer patients.Hereditas. 2022 Oct 18;159(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s41065-022-00253-w. Hereditas. 2022. PMID: 36253800 Free PMC article.
-
TFRC, associated with hypoxia and immune, is a prognostic factor and potential therapeutic target for bladder cancer.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Feb 9;29(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01688-9. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38336764 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a novel mRNA-signature prediction model for prognosis of bladder cancer based on a statistical analysis.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jul 27;21(1):858. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08611-z. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34315402 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a tumor microenvironment-related seven-gene signature for predicting prognosis in bladder cancer.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 10;21(1):692. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08447-7. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34112144 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Development of a basement membrane gene signature and identification of the potential candidate therapeutic targets for pancreatic cancer.Gland Surg. 2023 Feb 28;12(2):263-281. doi: 10.21037/gs-23-24. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Gland Surg. 2023. PMID: 36915817 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of molecular subtypes based on chromatin regulators and identification of the role of NPAS2 in lung adenocarcinoma.Clin Epigenetics. 2023 Apr 29;15(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13148-023-01486-w. Clin Epigenetics. 2023. PMID: 37120564 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin regulators-related lncRNA signature predicting the prognosis of kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and its relationship with immune microenvironment: A study based on bioinformatics and experimental validation.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 20;13:974726. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.974726. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36338996 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of molecular subtypes based on chromatin regulator and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in papillary renal cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Jan;149(1):231-245. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04482-4. Epub 2022 Nov 20. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36404389 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Chromatin Regulatory Factors Related to Immunity and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2023 Mar;73(2-3):85-94. doi: 10.1007/s12031-023-02107-0. Epub 2023 Feb 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36826468 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

