Cytoprotective gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 resolves major vessel occlusion disturbances, ischemia-reperfusion injury following Pringle maneuver, and Budd-Chiari syndrome
- PMID: 35125818
- PMCID: PMC8793015
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i1.23
Cytoprotective gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 resolves major vessel occlusion disturbances, ischemia-reperfusion injury following Pringle maneuver, and Budd-Chiari syndrome
Abstract
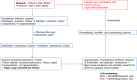
The stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 counteracts various venous occlusion-induced syndromes. Summarized are all these arguments, in the Robert's cytoprotection concept, to substantiate the resolution of different major vessel occlusion disturbances, in particular ischemia-reperfusion injury following the Pringle maneuver and Budd-Chiari syndrome, which was obtained by BPC 157 therapy. Conceptually, there is a new point, namely, endothelium maintenance to epithelium maintenance (the recruitment of collateral blood vessels to compensate for vessel occlusion and reestablish blood flow or bypass the occluded or ruptured vessel). In this paper, we summarize the evidence of the native cytoprotective gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157, which is stable in the human gastric juice, is a membrane stabilizer and counteracts gut-leaky syndrome. As a particular target, it is distinctive from the standard peptide growth factors, involving particular molecular pathways and controlling VEGF and NO pathways. In the early 1990s, BPC 157 appeared as a late outbreak of the Robert's and Szabo's cytoprotection-organoprotection concept, like the previous theoretical/practical breakthrough in the 1980s and the brain-gut axis and gut-brain axis. As the time went on, with its reported effects, it is likely most useful theory practical implementation and justification. Meantime, several reviews suggest that BPC 157, which does not have a lethal dose, has profound cytoprotective activity, used to be demonstrated in ulcerative colitis and multiple sclerosis trials. Likely, it may bring the theory to practical application, starting with the initial argument, no degradation in human gastric juice for more than 24 h, and thereby, the therapeutic effectiveness (including via a therapeutic per-oral regimen) and pleiotropic beneficial effects.
Keywords: Budd-Chiari syndrome; Cytoprotection; Gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157; Major vessel occlusion disturbances; Pringle maneuver; Therapy.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Sikiric P, Hahm KB, Blagaic AB, Tvrdeic A, Pavlov KH, Petrovic A, Kokot A, Gojkovic S, Krezic I, Drmic D, Rucman R, Seiwerth S. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157, Robert's stomach cytoprotection/adaptive cytoprotection/organoprotection, and Selye's stress coping response: Progress, achievements, and the future. Gut Liver. 2020;14:153–167. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sikiric P, Seiwerth S, Rucman R, Kolenc D, Vuletic LB, Drmic D, Grgic T, Strbe S, Zukanovic G, Crvenkovic D, Madzarac G, Rukavina I, Sucic M, Baric M, Starcevic N, Krstonijevic Z, Bencic ML, Filipcic I, Rokotov DS, Vlainic J. Brain-gut axis and pentadecapeptide BPC 157: Theoretical and practical implications. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2016;14:857–865. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seiwerth S, Milavic M, Vukojevic J, Gojkovic S, Krezic I, Vuletic LB, Pavlov KH, Petrovic A, Sikiric S, Vranes H, Prtoric A, Zizek H, Durasin T, Dobric I, Staresinic M, Strbe S, Knezevic M, Sola M, Kokot A, Sever M, Lovric E, Skrtic A, Blagaic AB, Sikiric P. Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157 and wound healing. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:627533. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gwyer D, Wragg NM, Wilson SL. Gastric pentadecapeptide body protection compound BPC 157 and its role in accelerating musculoskeletal soft tissue healing. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;377:153–159. - PubMed
-
- Kang EA, Han YM, An JM, Park YJ, Sikiric P, Kim DH, Kwon KA, Kim YJ, Yang D, Tchah H, Hahm KB. BPC157 as potential agent rescuing from cancer cachexia. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24:1947–1956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

