Increased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid During the Acute Phase in TBI-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in the Rat Model
- PMID: 35125890
- PMCID: PMC8809523
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S344110
Increased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid During the Acute Phase in TBI-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in the Rat Model
Abstract
Background: The present study aimed to develop a rat model for mechanical allodynia after traumatic brain injury (TBI) and to investigate the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) using this model.
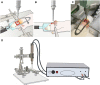
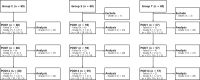
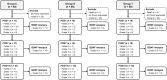
Methods: A total of 180 rats were randomly allocated into three groups: a control group (group C), a sham-operated group (group S), and a controlled cortical impact induced TBI group (group T), 60 in each group. Von Frey test was performed to evaluate mechanical withdrawal thresholds. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was performed to quantify BDNF level in CSF.
Results: The 50% withdrawal thresholds of group T were lower than those of group C and group S at all measuring points except for the preoperative period (P = 0.026, <0.001, and <0.001 for POD1, POD7, and POD14, respectively). The BDNF level of group T was higher than those of group C and group S at POD1 (P = 0.005).
Conclusion: Upregulation of the BDNF expression in CSF was observed in rats who developed mechanical allodynia on the day after TBI. Based on our findings, to elucidate the relationship between TBI-induced neuropathic pain and BDNF expression in CSF, further research should be carried out through a multifaceted approach to a broad spectrum of pain behavior models.
Keywords: animal; brain injuries; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; models; nerve growth factors; neuralgia; traumatic.
© 2022 Do et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Dr. Wangseok Do reports grants from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT), during the conduct of the study. Dr Soeun Jeon reports grants from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT), during the conduct of the study. Dr Chang-Min You reports grants from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT), during the conduct of the study. Dr Dahyun Kang reports grants from National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (Ministry of Science and ICT), during the conduct of the study. Dr Jiyoon Lee reports grants from Pusan National University Hospital, grants from Korean government, during the conduct of the study. The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intrathecal dexmedetomidine attenuates mechanical allodynia through the downregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in a mild traumatic brain injury rat model.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023 Feb;76(1):56-66. doi: 10.4097/kja.22209. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 35760392 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Intrathecal Ketamine on Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Feb 1;30:e942574. doi: 10.12659/MSM.942574. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38297827 Free PMC article.
-
The implication of transient receptor potential canonical 6 in BDNF-induced mechanical allodynia in rat model of diabetic neuropathic pain.Life Sci. 2021 May 15;273:119308. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119308. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33667520
-
Chronic Sciatic Neuropathy in Rat Reduces Voluntary Wheel-Running Activity With Concurrent Chronic Mechanical Allodynia.Anesth Analg. 2017 Jan;124(1):346-355. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001662. Anesth Analg. 2017. PMID: 27782944 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting BDNF/TrkB.T1 receptor improves resiniferatoxin-induced postherpetic neuralgia through decreasing ASIC3 signaling in dorsal root ganglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Apr 19;18(1):96. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02148-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 33874962 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intrathecal dexmedetomidine attenuates mechanical allodynia through the downregulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in a mild traumatic brain injury rat model.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023 Feb;76(1):56-66. doi: 10.4097/kja.22209. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 35760392 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF: New Views of an Old Player in Traumatic Brain Injury.Neuroscientist. 2024 Oct;30(5):560-573. doi: 10.1177/10738584231164918. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Neuroscientist. 2024. PMID: 37067029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurotrophins and neural stem cells in posttraumatic brain injury repair.Animal Model Exp Med. 2024 Feb;7(1):12-23. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12363. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Animal Model Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38018458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Intrathecal Ketamine on Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Mild Traumatic Brain Injury.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Feb 1;30:e942574. doi: 10.12659/MSM.942574. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38297827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jung HY, Han SH. Depression after traumatic brain injury. Korean J Biol Psychiatry. 1999;6(1):21–29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

