Acute Oral, Subacute, and Developmental Toxicity Profiling of Naphthalene 2-Yl, 2-Chloro, 5-Nitrobenzoate: Assessment Based on Stress Response, Toxicity, and Adverse Outcome Pathways
- PMID: 35126145
- PMCID: PMC8811508
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.810704
Acute Oral, Subacute, and Developmental Toxicity Profiling of Naphthalene 2-Yl, 2-Chloro, 5-Nitrobenzoate: Assessment Based on Stress Response, Toxicity, and Adverse Outcome Pathways
Abstract
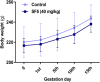
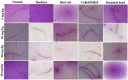
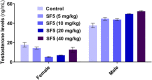
The U.S. National Research Council (NRC) introduced new approaches to report toxicity studies. The NRC vision is to explore the toxicity pathways leading to the adverse effects in intact organisms by the exposure of the chemicals. This study examines the toxicity profiling of the naphthalene-2-yl 2-chloro-5-dinitrobenzoate (SF5) by adopting the vision of NRC that moves from traditional animal studies to the cellular pathways. Acute, subacute, and developmental toxicity studies were assayed according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) guidelines. The stress response pathway, toxicity pathway, and adverse effects outcome parameters were analyzed by using their standard protocols. The results showed that the acute toxicity study increases the liver enzyme levels. In a subacute toxicity study, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels were raised in both male and female animals. SF5 significantly increases the normal sperm count in the male animals corresponding to a decrease in the abnormality count. Developmental toxicity showed the normal skeletal and morphological parameters, except little hydrocephalus was observed in developmental toxicity. Doses of 20 mg/kg in males and 4 mg/kg in females showed decreased glutathione (GSH) levels in the kidney and liver. MDA levels were also increased in the kidney and liver. However, histopathological studies did not show any cellular change in these organs. No statistical difference was observed in histamine levels, testosterone, nuclear factor erythroid two-related factor-2 (Nrf2), and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), which showed no initiation of the stress response, toxicity, and adverse effect pathways. Immunomodulation was observed at low doses in subacute toxicity studies. It was concluded that SF5 did not produce abrupt and high-toxicity levels in organs and biochemical parameters. So, it is safe for further studies.
Keywords: Nrf2; SF5; acute oral toxicity; biochemical parameters; oxidative stress markers; stress response pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Anwar, Saleem, rehman, Ahmad, Ismail, Mirza and Ahmad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures











Similar articles
-
Toxicity Evaluation of the Naphthalen-2-yl 3,5-Dinitrobenzoate: A Drug Candidate for Alzheimer Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 May 10;12:607026. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.607026. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34040515 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicological Screening of 4-Phenyl-3,4-dihydrobenzo[h]quinolin-2(1H)-one: A New Potential Candidate for Alzheimer's Treatment.ACS Omega. 2021 Apr 16;6(16):10897-10909. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c00654. eCollection 2021 Apr 27. ACS Omega. 2021. Retraction in: ACS Omega. 2024 Sep 06;9(37):39296. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c08066. PMID: 34056243 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Phytochemical and toxicological evaluation of Zephyranthes citrina.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 23;13:1007310. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1007310. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36210854 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18328408 Review.
-
Toxicity testing in the 21 century: defining new risk assessment approaches based on perturbation of intracellular toxicity pathways.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020887. Epub 2011 Jun 20. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21701582 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Safety assessment of novel oxadiazole derivatives in acute and sub-acute toxicity studies.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):3631-3653. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03474-0. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39352536
-
Acute, chronic, and genotoxic studies on the protopine total alkaloids of the Macleaya cordata (willd.) R. Br. in rodents.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 28;13:987800. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.987800. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36249819 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-arthritic and toxicological evaluation of ethanolic extract of Alternanthera bettzickiana in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 24;13:1002037. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1002037. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36353479 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic effects of Brugmansia aurea leaf extract by modulating the glucose levels, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress mechanism.Front Nutr. 2022 Oct 11;9:1005341. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1005341. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36304231 Free PMC article.
-
Solanum nigrum L. in COVID-19 and post-COVID complications: a propitious candidate.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 Oct;478(10):2221-2240. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04654-3. Epub 2023 Jan 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36689040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abozeid M. A., El-Sawi A. A., Abdelmoteleb M., Awad H., Abdel-Aziz M. M., Hassan Abdel-Rahman A.-R., et al. (2020). Synthesis of Novel Naphthalene-Heterocycle Hybrids with Potent Antitumor, Anti-inflammatory and Antituberculosis Activities. RSC Adv. 10 (70), 42998–43009. 10.1039/d0ra08526j - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anwar F., Saleem U., Ahmad B., Ashraf M., Rehman A. U., Froeyen M., et al. (2020). New Naphthalene Derivative for Cost-Effective AChE Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Treatment: In Silico Identification, In Vitro and In Vivo Validation. Comput. Biol. Chem. 89, 107378. 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107378 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

