Macular Edema and Visual Acuity Observation after Cataract Surgery in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
- PMID: 35126918
- PMCID: PMC8808216
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3311751
Macular Edema and Visual Acuity Observation after Cataract Surgery in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
Objective: The purpose was to explore the effect of cataract surgery on postoperative macular edema and visual acuity in patients with diabetic retinopathy.
Methods: 88 patients with diabetic retinopathy treated in our hospital (December 2019-December 2020) were chosen as research subjects and divided into experimental group of 44 patients (52 eyes) and control group of 44 patients (54 eyes) according to the odd and even admission numbers. The control group received laser photocoagulation treatment, while the experimental group underwent cataract surgery. The central macular thickness (CMT) and visual acuity of the two groups after treatment were detected to evaluate the therapeutic effect of different treatment methods on diabetic retinopathy.
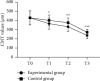
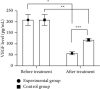
Results: No obvious differences in sex ratio, average age, average course of disease, average weight, average BMI, average glycosylated hemoglobin, and residence were found between the two groups (P > 0.05). The total clinical effective rate in the experimental group was obviously higher compared with the control group (P < 0.05). The CMT at T1, T2, and T3 in the experimental group was obviously lower compared with the control group (P < 0.05). The BCVA in the experimental group at 1 month and 3 months after treatment was obviously higher compared with the control group (P < 0.05). The VEGF levels of both groups after treatment were obviously lower (P < 0.001), and the VEGF level in the experimental group after treatment was obviously lower compared with the control group (P < 0.001). The total incidence of complications in the experimental group was obviously lower compared with the control group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Cataract surgery is a reliable method to improve visual acuity and reduce serum inflammatory indicators in patients with diabetic retinopathy, with better clinical effect than laser photocoagulation, which is recommended for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
Copyright © 2022 Ruiying Song et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phacoemulsification with intravitreal bevacizumab injection in diabetic patients with macular edema and cataract.Retina. 2009 Nov-Dec;29(10):1432-5. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181b77422. Retina. 2009. PMID: 19898181
-
Does conventional laser photocoagulation still have a place in the treatment of diabetic macular edema?Rom J Ophthalmol. 2021 Apr-Jun;65(2):130-135. doi: 10.22336/rjo.2021.27. Rom J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34179577 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal bevacizumab and/or macular photocoagulation as a primary treatment for diffuse diabetic macular edema.Retina. 2010 Nov-Dec;30(10):1638-45. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0b013e3181e1ed07. Retina. 2010. PMID: 20838357 Clinical Trial.
-
Diabetic maculopathy and cataract surgery.Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001 Dec;14(4):625-37. doi: 10.1016/s0896-1549(05)70262-5. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2001. PMID: 11787742 Review.
-
The management of cataract surgery in diabetic patients.J Perioper Pract. 2022 Dec;32(12):361-367. doi: 10.1177/17504589221091063. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Perioper Pract. 2022. PMID: 35445624 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence method based on multi-feature fusion for automatic macular edema (ME) classification on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) images.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jan 30;17:1097291. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1097291. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36793539 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rose M. A., Vukicevic M., Koklanis K., Rees G., Sandhu S., Itsiopoulos C. Experiences and perceptions of patients undergoing treatment and quality of life impact of diabetic macular edema: a systematic review. Psychology Health & Medicine . 2019;24(4):383–401. doi: 10.1080/13548506.2018.1533249. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suhner A., Lin R., Wolf S., et al. Efficacy and safety of ranibizumab 0.5 mg in Chinese patients with visual impairment due to diabetic macular edema: results from the 12-month REFINE study. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology: Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fur Klinische und Experimentelle Opthalmologie . 2019;257(3):529–541. doi: 10.1007/s00417-018-04213-x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

