Mechanism of high affinity potassium transporter (HKT) towards improved crop productivity in saline agricultural lands
- PMID: 35127306
- PMCID: PMC8795266
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-021-03092-0
Mechanism of high affinity potassium transporter (HKT) towards improved crop productivity in saline agricultural lands
Abstract
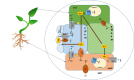
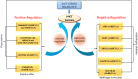
Glycophytic plants are susceptible to salinity and their growth is hampered in more than 40 mM of salt. Salinity not only affects crop yield but also limits available land for farming by decreasing its fertility. Presence of distinct traits in response to environmental conditions might result in evolutionary adaptations. A better understanding of salinity tolerance through a comprehensive study of how Na+ is transported will help in the development of plants with improved salinity tolerance and might lead to increased yield of crops growing in strenuous environment. Ion transporters play pivotal role in salt homeostasis and maintain low cytotoxic effect in the cell. High-affinity potassium transporters are the critical class of integral membrane proteins found in plants. It mainly functions to remove excess Na+ from the transpiration stream to prevent sodium toxicity in the salt-sensitive shoot and leaf tissues. However, there are large number of HKT proteins expressed in plants, and it is possible that these members perform in a wide range of functions. Understanding their mechanism and functions will aid in further manipulation and genetic transformation of different crops. This review focuses on current knowledge of ion selectivity and molecular mechanisms controlling HKT gene expression. The current review highlights the mechanism of different HKT transporters from different plant sources and how this knowledge could prove as a valuable tool to improve crop productivity.
Keywords: High-affinity potassium transporter (HKT); Ion homeostasis; Salinity stress; Sodium transport.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plant High-Affinity Potassium (HKT) Transporters involved in salinity tolerance: structural insights to probe differences in ion selectivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr 9;14(4):7660-80. doi: 10.3390/ijms14047660. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23571493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To exclude or to accumulate? Revealing the role of the sodium HKT1;5 transporter in plant adaptive responses to varying soil salinity.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Dec;169:333-342. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.11.030. Epub 2021 Nov 19. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34837866 Review.
-
HKT transporters mediate salt stress resistance in plants: from structure and function to the field.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015 Apr;32:113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2014.11.025. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25528276 Review.
-
HKT transporter-mediated salinity resistance mechanisms in Arabidopsis and monocot crop plants.Trends Plant Sci. 2009 Dec;14(12):660-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2009.08.009. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Trends Plant Sci. 2009. PMID: 19783197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K(+)/Na(+) ratio in leaves during salinity stress.Plant Cell Environ. 2010 Apr;33(4):552-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.02056.x. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Plant Cell Environ. 2010. PMID: 19895406 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in deciphering the mechanisms of salt tolerance in Maize.Plant Signal Behav. 2025 Dec;20(1):2479513. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2025.2479513. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Plant Signal Behav. 2025. PMID: 40098499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the High-Affinity Potassium Transporter Gene Family (HKT) in Brassica U-Triangle Species and Its Potential Roles in Abiotic Stress in Brassica napus L.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 4;12(21):3768. doi: 10.3390/plants12213768. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37960124 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and network analysis pinpoint ABA and plastid ribosomal proteins as main contributors to salinity tolerance in the rice variety, CSR28.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 17;20(4):e0321181. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321181. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40244966 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Photosynthesis and Plant Productivity through Genetic Modification.Cells. 2024 Aug 7;13(16):1319. doi: 10.3390/cells13161319. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39195209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-locus genome-wide association studies reveal genomic regions associated with sodicity tolerance in rice.Plant Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 21;115(4):88. doi: 10.1007/s11103-025-01622-5. Plant Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40690060
References
-
- Abdulhussein F, Mutlag N, Sarheed A. Genotypic characterization and tissue localization of the mutant lines expression of HKT1; 3 gene in rice under salt stress. Plant Arch. 2018;18(1):489–495.
-
- Acosta-Motos JR, Ortuño MF, Bernal-Vicente A, Diaz-Vivancos P, Sanchez-Blanco MJ, Hernandez JA. Plant responses to salt stress: adaptive mechanisms. Agronomy. 2017;7(1):18.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

