Performance evaluation of publish-subscribe systems in IoT using energy-efficient and context-aware secure messages
- PMID: 35127310
- PMCID: PMC8802267
- DOI: 10.1186/s13677-022-00278-6
Performance evaluation of publish-subscribe systems in IoT using energy-efficient and context-aware secure messages
Abstract
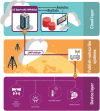
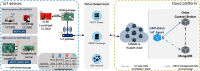
Background: The Internet of Things (IoT) enables the development of innovative applications in various domains such as healthcare, transportation, and Industry 4.0. Publish-subscribe systems enable IoT devices to communicate with the cloud platform. However, IoT applications need context-aware messages to translate the data into contextual information, allowing the applications to act cognitively. Besides, end-to-end security of publish-subscribe messages on both ends (devices and cloud) is essential. However, achieving security on constrained IoT devices with memory, payload, and energy restrictions is a challenge.
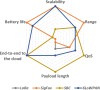
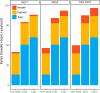
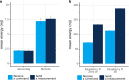
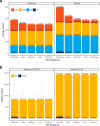
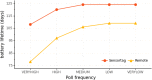
Contribution: Messages in IoT need to achieve both energy efficiency and secure delivery. Thus, the main contribution of this paper refers to a performance evaluation of a message structure that standardizes the publish-subscribe topic and payload used by the cloud platform and the IoT devices. We also propose a standardization for the topic and payload for publish-subscribe systems.
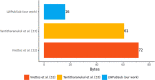
Conclusion: The messages promote energy efficiency, enabling ultra-low-power and high-capacity devices and reducing the bytes transmitted in the IoT domain. The performance evaluation demonstrates that publish-subscribe systems (namely, AMQP, DDS, and MQTT) can use our proposed energy-efficient message structure on IoT. Additionally, the message system provides end-to-end confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity between IoT devices and the cloud platform.
Keywords: Context-aware messages; IoT; Publish-subscribe; Security; WSN.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Almutairi J, Aldossary M. A novel approach for IoT tasks offloading in edge-cloud environments. J Cloud Comput. 2021;10(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13677-021-00243-9. - DOI
-
- Ni J, Lin X, Shen XS. Toward Edge-Assisted Internet of Things: From Security and Efficiency Perspectives. IEEE Netw. 2019;33(2):50–7. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2019.1800229. - DOI
-
- Al-Fuqaha A, Guizani M, Mohammadi M, Aledhari M, Ayyash M. Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor. 2015;17(4):2347–76. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2444095. - DOI
-
- Asghari P, Rahmani AM, Javadi HHS. Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Comput Netwo. 2019;148:241–61. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2018.12.008. - DOI
-
- Du X, Zhou Z, Zhang Y, Rahman T (2020) Energy-efficient sensory data gathering based on compressed sensing in IoT networks. J Cloud Comput 9(1). 10.1186/s13677-020-00166-x.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
