The Role of Circulating Biomarkers in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 35127511
- PMCID: PMC8813755
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.801269
The Role of Circulating Biomarkers in Lung Cancer
Abstract
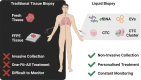
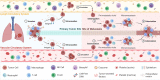
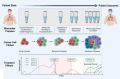
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer morbidity and mortality worldwide and early diagnosis is crucial for the management and treatment of this disease. Non-invasive means of determining tumour information is an appealing diagnostic approach for lung cancers as often accessing and removing tumour tissue can be a limiting factor. In recent years, liquid biopsies have been developed to explore potential circulating tumour biomarkers which are considered reliable surrogates for understanding tumour biology in a non-invasive manner. Most common components assessed in liquid biopsy include circulating tumour cells (CTCs), cell-free DNA (cfDNA), circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA), microRNA and exosomes. This review explores the clinical use of circulating tumour biomarkers found in liquid biopsy for screening, early diagnosis and prognostication of lung cancer patients.
Keywords: Circulating tumour cells; cell-free DNA; circulating tumour DNA; liquid biopsy; lung cancer; microRNA and exosomes.
Copyright © 2022 Herath, Sadeghi Rad, Radfar, Ladwa, Warkiani, O’Byrne and Kulasinghe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Brest A, Yu M, et al. . SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2017. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute; (2020) https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2017/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

