A Comparison of Beclomethasone Aqueous Spray and Aerosol Delivery System in Nasal Polyps: A Randomized Control Trial
- PMID: 35127578
- PMCID: PMC8781911
- DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_30_20
A Comparison of Beclomethasone Aqueous Spray and Aerosol Delivery System in Nasal Polyps: A Randomized Control Trial
Abstract
Background: Considering the effect of beclomethasone on allergic rhinitis or nasal polyps, it has been attempted to find the best method of using this drug to have the maximum effect and increase the patients' satisfaction. Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of beclomethasone aerosol and aqueous nasal sprays in the patients with nasal polyps.
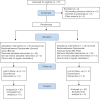
Materials and methods: This double-blind randomized clinical trial was conducted on 60 patients with nasal polyps. The patients were divided into two groups. The first group (beclomethasone dipropionate aqueous [BD-AQ] group) was treated with daily two puffs of beclomethasone aqueous nasal spray 50 μg in each nostril, and the second group (beclomethasone dipropionate aerosol [BD-A] group) was treated with two puffs of aerosol beclomethasone 50 μg in each nostril daily for 6 months. At the beginning of the study, the sino-nasal outcome test-22 (SNOT-22) and Lund-Mackay scores were recorded after the evaluation of disease status and the severity of symptoms.
Results: The results of this study demonstrated that the mean changes in Lund-Mackay and SNOT-22 scores (83 ± 6.30 and 4.25 ± 31.60, respectively) in the BD-A group were significantly higher than the BD-AQ group (2.01 ± 3.87and 9.83 ± 24.13, respectively) (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in the patients' satisfaction between the two groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion: According to the results of this study, patients with nasal polyps showed a significant improvement following both the interventions, but the disease severity in the BD-A group was significantly higher than the BD-AQ group based on the mean values of Lund-Mackay score.
Keywords: Aerosols; Blood-Aqueous Barrier; beclomethasone; nasal polyps.
Copyright: © 2021 Advanced Biomedical Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dykewicz MS, Hamilos DL. Rhinitis and sinusitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125:S103–15. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. EPOS 2012: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology. 2012;50:1–2. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
