Engraftment, Fate, and Function of HoxB8-Conditional Neutrophil Progenitors in the Unconditioned Murine Host
- PMID: 35127689
- PMCID: PMC8812959
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.840894
Engraftment, Fate, and Function of HoxB8-Conditional Neutrophil Progenitors in the Unconditioned Murine Host
Abstract
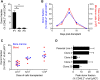
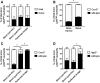
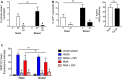
The development and use of murine myeloid progenitor cell lines that are conditionally immortalized through expression of HoxB8 has provided a valuable tool for studies of neutrophil biology. Recent work has extended the utility of HoxB8-conditional progenitors to the in vivo setting via their transplantation into irradiated mice. Here, we describe the isolation of HoxB8-conditional progenitor cell lines that are unique in their ability to engraft in the naïve host in the absence of conditioning of the hematopoietic niche. Our results indicate that HoxB8-conditional progenitors engraft in a β1 integrin-dependent manner and transiently generate donor-derived mature neutrophils. Furthermore, we show that neutrophils derived in vivo from transplanted HoxB8-conditional progenitors are mobilized to the periphery and recruited to sites of inflammation in a manner that depends on the C-X-C chemokine receptor 2 and β2 integrins, the same mechanisms that have been described for recruitment of endogenous primary neutrophils. Together, our studies advance the understanding of HoxB8-conditional neutrophil progenitors and describe an innovative tool that, by virtue of its ability to engraft in the naïve host, will facilitate mechanistic in vivo experimentation on neutrophils.
Keywords: cell therapeutics; engraftment; granulopoeisis; hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC); leukocyte recruitment; neutrophils.
Copyright © 2022 Cohen, Danise, Hinman, Neumann, Johnson, Wilson, Chorzalska, Dubielecka and Lefort.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

