A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges
- PMID: 35127995
- PMCID: PMC8806010
- DOI: 10.1007/s13337-022-00755-1
A comprehensive review on COVID-19 vaccines: development, effectiveness, adverse effects, distribution and challenges
Abstract
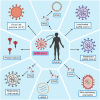
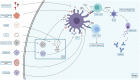
The present SARS-CoV-2 induced COVID-19 pandemic is responsible for millions of deaths, illnesses, and economic loss worldwide. There are 21 COVID-19 vaccines from different platforms approved worldwide for emergency use until 13 August 2021. Later, BNT162b2 obtained full approval from the FDA. The efficacy of the leading vaccines such as BNT162b2, mRNA-1273, Gam-Covid-Vac, Ad26.COV2.S, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, and BBIBP-CorV, against SARS-CoV-2 documented as 95%, 94.1%, 91.6%, 67%, 70.4%, and 78.1%, respectively. Moreover, against the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2, BNT162b2, ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, and BBV152 showed 88%, 70%, and 65.2% efficacy, respectively. Apart from the common adverse effects such as fever, fatigue, headache, and pain in the injection site, Bell's palsy with BNT162b2, myocarditis and pericarditis with mRNA-1273, and thrombosis with ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 have been reported though seemed not alarming. Furthermore, global production and distribution of vaccines should be ensured in an equal and justifiable way that the immunity and protection against the virus would be optimum and persistent.
Keywords: Adverse effects; COVID-19 vaccines; Distribution; Effectiveness; Immunogenicity; SARS-CoV-2.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Indian Virological Society 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- AstraZeneca. AZD1222 US Phase III trial met primary efficacy endpoint in preventing COVID-19 at interim analysis. https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2021/astrazeneca.... 2021a. Accessed 13 August 2021.
-
- AstraZeneca. Vaxzevria is highly effective after one dose against severe disease or hospitalisation caused by Beta and Delta variants of concern. https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2021/vaxzevria-i.... 2021b. Accessed 13 August 2021.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

