Targeting the Inflammasome in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 35128212
- PMCID: PMC8807732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.08.006
Targeting the Inflammasome in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
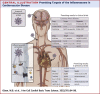
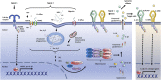
The pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease (CVD) is complex and multifactorial, and inflammation plays a central role. Inflammasomes are multimeric protein complexes that are activated in a 2-step manner in response to infection or tissue damage. Upon activation the proinflammatory cytokines, interleukins-1β and -18 are released. In the last decade, the evidence that inflammasome activation plays an important role in CVD development became stronger. We discuss the role of different inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of CVD, focusing on atherosclerosis and heart failure. This review also provides an overview of existing experimental studies and clinical trials on inflammasome inhibition as a therapeutic target in these disorders.
Keywords: ACS, acute coronary syndrome; AIM2, absent in melanoma 2; ASC, apoptosis associated speck-like protein; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CAD, coronary artery disease; CRP, C-reactive protein; CVD, cardiovascular disease; DAMP, damage associated molecular pattern; GSDMD, gasdermin-D; GSDMD-NT, gasdermin-D N-terminal; HF, heart failure; HFpEF, HF with preserved ejection fraction; HFrEF, HF with reduced ejection fraction; IL, interleukin; IL-1; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LV, left ventricular; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; MI, myocardial infarction; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NLR, NOD-like receptor; NLRP3; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3; NOD, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; PRR, pattern recognition receptor; STEMI, ST-elevation myocardial infarction; TLR, toll-like receptor; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; heart failure; inflammasome.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority (grant 2019058 to Dr Louwe) and Throne-Holst fund (grant 511322 to Dr Belland Olsen). Dr Sokolova is currently an employee of GlaxoSmithKline. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

