The additional diagnostic value of motor nerve excitability testing in chronic axonal neuropathy
- PMID: 35128215
- PMCID: PMC8803553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cnp.2021.12.001
The additional diagnostic value of motor nerve excitability testing in chronic axonal neuropathy
Abstract
Objective: To explore potential differences in motor nerve excitability testing (NET) variables at group levels between patients with a clinical diagnosis of polyneuropathy (PNP), which did not fulfil diagnostic criteria of conventional nerve conduction studies (NCS) and patients without polyneuropathy. Such differences could support a role for NET in increasing the diagnostic sensitivity of NCS in chronic axonal PNP.
Methods: Motor NET was performed using the median nerve in patients with a clinical suspicion of PNP in addition to conventional NCS, skin biopsies, corneal confocal microscopy and structured clinical evaluation including scoring of neuropathy symptoms and signs.
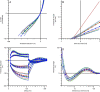
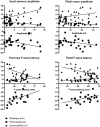
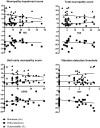
Results: Of the 57 patients included, 32 had PNP, half of which had NCS, which fulfilled criteria for PNP (NCS+ PNP). There were no significant differences for any of the NET variables between PNP patients with non-diagnostic conventional NCS (NCS- PNP) and patients without PNP. Rheobase was increased, and Ted (undershoot) and subexcitability were decreased in NCS+ PNP. Sural amplitude, peroneal nerve F-wave latency and tibial nerve F-wave-latency were correlated with subexcitability, and tibial nerve motor amplitude was correlated with rheobase.
Conclusions: NET was correlated with conventional NCS and no differences were found between NCS- PNP patients and patients without PNP.
Significance: NET does not seem to offer any additional diagnostic value in chronic mixed etiology neuropathy.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Nerve conduction studies; Nerve excitability testing; Polyneuropathy.
© 2022 International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic utility of distal nerve conduction studies and sural near-nerve needle recording in polyneuropathy.Clin Neurophysiol. 2017 Sep;128(9):1590-1595. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.031. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28710923
-
Sensory and motor axonal excitability testing in early diabetic neuropathy.Clin Neurophysiol. 2021 Jul;132(7):1407-1415. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2021.02.397. Epub 2021 Apr 8. Clin Neurophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34030050
-
Evidence-based recommendations for examination and diagnostic strategies of polyneuropathy electrodiagnosis.Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2019 Nov 18;4:214-222. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2019.10.005. eCollection 2019. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2019. PMID: 31886447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Standard Clinical Screening Tests, Sural Radial Amplitude Ratio and F Wave Latency Compared to Conventional Nerve Conduction Studies in the Assessment of Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Nov-Dec;25(6):509-515. doi: 10.4103/ijem.ijem_426_21. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 35355904 Free PMC article.
-
Electrodiagnosis of polyneuropathy.Neurophysiol Clin. 2000 Dec;30(6):339-51. doi: 10.1016/s0987-7053(00)00237-9. Neurophysiol Clin. 2000. PMID: 11191927 Review.
Cited by
-
The test-retest reliability of large and small fiber nerve excitability testing with threshold tracking.Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2023 Mar 30;8:71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2023.03.003. eCollection 2023. Clin Neurophysiol Pract. 2023. PMID: 37181417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouhassira D., Attal N., Fermanian J., Alchaar H., Gautron M., Masquelier E., Rostaing S., Lanteri-Minet M., Collin E., Grisart J., Boureau F. Development and validation of the Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory. Pain. 2004;108:248–257. - PubMed
-
- Cappelen-Smith C., Kuwabara S., Lin C.S.Y., Mogyoros I., Burke D. Membrane properties in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Brain. 2001;124:2439–2447. - PubMed
-
- Cavaletti G., Bogliun G., Marzorati L., Zincone A., Piatti M., Colombo N., Parma G., Lissoni A., Fei F., Cundari S., Zanna C. Grading of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity using the Total Neuropathy Scale. Neurology. 2003;61(9):1297–1300. - PubMed
-
- Dyck P.J., Sherman W.R., Hallcher L.M., John Service F., O'Brien P.C., Grina L.A., Palumbo P.J., Swanson C.J. Human diabetic endoneurial sorbitol, fructose, and myo-inositol related to sural nerve morphometry. Ann. Neurol. 1980;8(6):590–596. - PubMed
-
- Dyck P.J., Boes C.J., Mulder D., Millikan C., Windebank A.J., Dyck P.J.B., Espinosa R. History of standard scoring, notation, and summation of neuromuscular signs. A current survey and recommendation. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2005;10(2):158–173. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

