Role of inhibitory signaling in peripheral B cell tolerance
- PMID: 35128676
- PMCID: PMC8986582
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.13070
Role of inhibitory signaling in peripheral B cell tolerance
Abstract
At least 20% of B cells in the periphery expresses an antigen receptor with a degree of self-reactivity. If activated, these autoreactive B cells pose a risk as they can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases. To prevent their activation, both B cell-intrinsic and extrinsic tolerance mechanisms are in place in healthy individuals. In this review article, I will focus on B cell-intrinsic mechanisms that prevent the activation of autoreactive B cells in the periphery. I will discuss how inhibitory signaling circuits are established in autoreactive B cells, focusing on the Lyn-SHIP-1-SHP-1 axis, how they contribute to peripheral immune tolerance, and how disruptions of these circuits can contribute to the development of autoimmunity.
Keywords: B cells; autoimmunity; protein kinases/phosphatases; signal transduction; tolerance/suppression/anergy.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
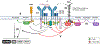

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

