A Multi-Task Learning Framework for Automated Segmentation and Classification of Breast Tumors From Ultrasound Images
- PMID: 35128997
- PMCID: PMC8902030
- DOI: 10.1177/01617346221075769
A Multi-Task Learning Framework for Automated Segmentation and Classification of Breast Tumors From Ultrasound Images
Abstract
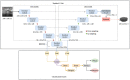
Breast cancer is one of the most fatal diseases leading to the death of several women across the world. But early diagnosis of breast cancer can help to reduce the mortality rate. So an efficient multi-task learning approach is proposed in this work for the automatic segmentation and classification of breast tumors from ultrasound images. The proposed learning approach consists of an encoder, decoder, and bridge blocks for segmentation and a dense branch for the classification of tumors. For efficient classification, multi-scale features from different levels of the network are used. Experimental results show that the proposed approach is able to enhance the accuracy and recall of segmentation by , , and classification by , , respectively than the methods available in the literature.
Keywords: benign; breast cancer; classification; malignant; multi-task learning; segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394-424. - PubMed
-
- IARC. IARC Biennial Report 2020-2021. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available from: https://publications.iarc.fr/607
-
- Islami F, Goding Sauer A, Miller KD, Siegel RL, Fedewa SA, Jacobs EJ, et al.. Proportion and number of cancer cases and deaths attributable to potentially modifiable risk factors in the United States. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:31-54. - PubMed
-
- Anitha J, Peter JD. Mammogram segmentation using maximal cell strength updation in cellular automata. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2015;53:737-49. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

