DNA methyltransferase 3 beta regulates promoter methylation of microRNA-149 to augment esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development through the ring finger protein 2/Wnt/β-catenin axis
- PMID: 35129056
- PMCID: PMC8973842
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2031411
DNA methyltransferase 3 beta regulates promoter methylation of microRNA-149 to augment esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development through the ring finger protein 2/Wnt/β-catenin axis
Abstract
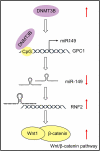
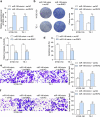
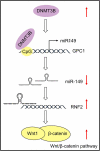
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is an aggressive form of human squamous cell carcinomas with extremely aggressive pathological features. This study explores the functions of microRNA-149 (miR-149) and its interacted molecules in ESCC. The ESCC-related miRNA and messenger RNA (mRNA) datasets were applied to identify aberrantly expressed genes in ESCC. Forty-two patients with ESCC were included and their tissue samples were collected. miR-149 was poorly expressed whereas DNA methyltransferase 3 beta (DNMT3B) and ring finger protein 2 (RNF2) were abundantly expressed in ESCC tumor samples. Overexpression of miR-149 suppressed growth and invasiveness of ESCC cells in vitro and in vivo. DNMT3B bound to the promoter region of miR-149 to trigger its promoter methylation and downregulation. RNF2 mRNA was a target of miR-149. RNF2 overexpression blocked the inhibitory effect of miR-149 on ESCC cell growth. RNF2 activated the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to promote ESCC development. In conclusion, this study found that DNMT3B downregulates miR-149 level through methylation modification of the miR-149 promoter, while miR-149 suppresses RNF2 expression and inactivates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway to suppress growth of ESCC cells.
Keywords: DNMT3B; Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; RNF2; methylation; miR-149; wnt/β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
