Effects of berbamine against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Activation of the 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor pathway and changes in the mitochondrial state
- PMID: 35129229
- PMCID: PMC9305777
- DOI: 10.1002/biof.1820
Effects of berbamine against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: Activation of the 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor pathway and changes in the mitochondrial state
Abstract
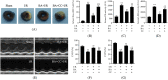
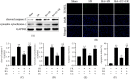
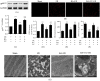
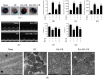
This study was designed to investigate whether berbamine (BA)-induced cardioprotective effects were related to 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2) signaling and changes in the mitochondria in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. C57/BL6 mice were exposed to BA (10 mg/kg/d), with or without administration of the AMPK specific inhibitor compound C (5 mg/kg/d) or the Nrf2 specific inhibitor ML-385 (30 mg/kg/d), and then subjected to a myocardial I/R operation. As expected, BA significantly improved post-ischemic cardiac function, reduced infarct size and apoptotic cell death, decreased oxidative stress, and improved the mitochondrial state. Furthermore, BA markedly increased AMPK activation, Nrf2 nuclear translocation, and the levels of NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase and heme oxygenase-1. Nevertheless, these BA-induced changes were abrogated by compound C. In addition, ML-385 also canceled the cardioprotective effects of BA but had little effect on AMPK activation. Our results demonstrate that BA alleviates myocardial I/R injury and the mitochondrial state by inhibiting apoptosis and oxidative stress via the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Keywords: AMPK/Nrf2; berbamine; heart; ischemia/reperfusion injury; mitochondrion; oxidative stress.
© 2022 The Authors. BioFactors published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Berbamine induced AMPK activation regulates mTOR/SREBP-1c axis and Nrf2/ARE pathway to allay lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in steatotic HepG2 cells.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 5;882:173244. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173244. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32526241
-
CaMKK2 alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation via the action on the AMPK-AKT-GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling cascade.Inflamm Res. 2023 Jul;72(7):1409-1425. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01756-6. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37338678
-
Activation of AMPK/p38/Nrf2 is involved in resveratrol alleviating myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats as an endogenous antioxidant stress feedback.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Aug;10(16):890. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3789. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36111006 Free PMC article.
-
AMPK and NRF2: Interactive players in the same team for cellular homeostasis?Free Radic Biol Med. 2022 Sep;190:75-93. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.07.014. Epub 2022 Jul 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35918013 Review.
-
AMPK, a key molecule regulating aging-related myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 1;51(1):257. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09050-8. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38302614 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in Chinese herbal medicine in modulating mitochondria to treat myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: a narrative review.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025 Feb 28;15(1):207-232. doi: 10.21037/cdt-24-346. Epub 2025 Feb 25. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2025. PMID: 40115104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Nanoparticles in the Prevention and Treatment of Myocardial Infarction.Molecules. 2024 May 21;29(11):2415. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112415. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardioprotective effects of asiaticoside against diabetic cardiomyopathy: Activation of the AMPK/Nrf2 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jan;28(2):e18055. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18055. Epub 2023 Dec 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38113341 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondria-Associated Organelle Crosstalk in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024 Oct;17(5):1106-1118. doi: 10.1007/s12265-024-10523-9. Epub 2024 May 28. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38807004 Review.
-
ELAVL1-dependent SOAT2 exacerbated the pancreatitis-like cellular injury of AR42J cells induced by hyperstimulation with caerulein.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025 Jan;41(1):e12911. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12911. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39588852 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Ren J. Targeting autophagy for the therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors in ischemia/reperfusion heart injury. Circulation. 2014;129(10):1088–91. - PubMed
-
- Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM. Ischaemic conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13(4):193–209. - PubMed
-
- Rossello X, Yellon DM. Cardioprotection: the disconnect between bench and bedside. Circulation. 2016;134(8):574–5. - PubMed
-
- Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(11):1121–35. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2020TD-034/Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province
- 2020YFC2008100/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 82000373/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82174493/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 20-205-4-039/Science and Technology Program of Shenyang
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

