A novel serum metabolomic panel distinguishes IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis
- PMID: 35129255
- PMCID: PMC9546203
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.15192
A novel serum metabolomic panel distinguishes IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis from primary sclerosing cholangitis
Abstract
Background & aims: Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis (IgG4-SC) are chronic fibro-inflammatory immune-mediated hepatobiliary conditions that are challenging to distinguish in a clinical setting. Accurate non-invasive biomarkers for discriminating PSC and IgG4-SC are important to ensure a correct diagnosis, prompt therapy and adequate cancer surveillance.
Methods: We performed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based metabolomic profiling using serum samples collected prospectively from patients with PSC (n = 100), IgG4-SC (n = 23) and healthy controls (HC; n = 16).
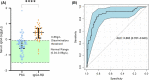
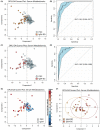
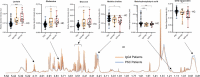
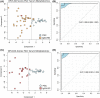
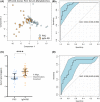
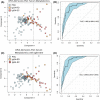
Results: Multivariate analysis of the serum metabolome discriminated PSC from IgG4-SC with greater accuracy (AUC 0.95 [95%CI 0.90-0.98]) than IgG4 titre (AUC 0.87 [95%CI 0.79-0.94]). When inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) was excluded as a comorbid condition (IgG4-SC n = 20, PSC n = 22), the diagnostic AUC increased to 1.0, suggesting that the metabolome differences identified are not a result of the increased prevalence of IBD in PSC relative to IgG4-SC patients. Serum lactate (p < .0001), glucose (p < .01) and glutamine (p < .01) metabolites were increased in IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) and IgG4-SC individuals compared to PSC, whereas mobile choline (p < .05), 3-hydroxybutyric acid (p < .01) and -CH3 lipoprotein resonances (p < .01) were decreased.
Conclusions: Taken together, serum metabolomic profiling has the potential to be incorporated as a diagnostic criterion, independent of IgG4 titre, to improve the diagnosis of IgG4-RD and help distinguish IgG4-SC from PSC.
Keywords: biomarkers; cholangitis; diagnosis; immunoglobulin G4-related disease; metabolomics; sclerosing.
© 2022 The Authors. Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
EAS, ELC, DERS, DCA, FP, RP, KDL, MO, JB, KL and AB declare no conflicts of interest. MP is a shareholder in Perspectum, a University of Oxford spin‐out company. AG was employed by UCB Celltech during the preparation of this manuscript and is now an employee of Glaxo Smith Kline (GSK).
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

