Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in metastatic colorectal cancer with contemporary treatment: A SEER-Medicare analysis
- PMID: 35129311
- PMCID: PMC9041082
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4581
Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in metastatic colorectal cancer with contemporary treatment: A SEER-Medicare analysis
Abstract
Background: The relationship between metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) is poorly defined in the modern era. Our objective was to examine impact of putative risk factors including newer treatments and anti-angiogenic therapy on VTE incidence and survival in a modern older mCRC cohort.
Methods: This is a SEER-Medicare cohort analysis of mCRC patients diagnosed in 2004-2009. Risk factor analysis was conducted using Cox models adjusted for sex, diagnosis age, race, primary tumor location, comorbidity, and prior VTE history, with cancer treatments as time-varying covariates. Main outcomes were VTE incidence and overall survival.
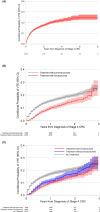
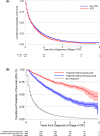
Results: Ten thousand nine hundred and seventy six mCRC cases with mean age 77.9 years (range 65-107), 49.7% women, 83.5% white. There were 1306 VTE cases corresponding to 13.7% incidence at 1 year and 20.3% at 3 years. Independent VTE predictors included female sex (HR 1.27; 95% CI 1.14-1.42), African American race (HR 1.49; 1.27-1.73), prior VTE history (HR 16.3; 12.1-22.1), and right sided cancers (HR 1.16; 1.04-1.29). After adjustment, any therapy and bevacizumab (HR 0.68, 0.58-0.78) in particular were protective. Overall survival was 40.1% (39.4-41.3) at 1 year but improved significantly with any treatment. VTE following diagnosis of mCRC was associated with inferior OS (HR 1.09; 1.02-1.15).
Conclusions: In this large contemporary mCRC cohort, effective systemic therapy including anti-angiogenic treatment was associated with lower VTE risk. Overall survival was poor, and modestly worse if a patient had a VTE at any time during treatment.
Keywords: bevacizumab; cohort studies; colonic neoplasms; survival analysis; venous thromboembolism.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no relevant COI disclosures for any of the contributing authors.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(1):7‐34. - PubMed
-
- Yoo PS, Lopez‐Soler RI, Longo WE, Cha CH. Liver resection for metastatic colorectal cancer in the age of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and bevacizumab. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2006;6(3):202‐207. - PubMed
-
- Lee WS, Yun SH, Chun HK, et al. Pulmonary resection for metastases from colorectal cancer: prognostic factors and survival. Int J Color Dis 2007;22(6):699–704. - PubMed
-
- Ades S, Kumar S, Alam M, et al. Tumor oncogene (KRAS) status and risk of venous thrombosis in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Thromb Haemost 2015;13(6):998–1003. - PubMed
-
- Timp JF, Braekkan SK, Versteeg HH, Cannegieter SC. Epidemiology of cancer‐associated venous thrombosis. Blood. 2013;122(10):1712‐1723. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

