Delphinidin-3- O-glucoside, an active compound of Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces, inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in rabbits with atherosclerosis
- PMID: 35130117
- PMCID: PMC8823684
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2021.2017469
Delphinidin-3- O-glucoside, an active compound of Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces, inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation in rabbits with atherosclerosis
Abstract
Context: Delphinidin-3-O-glucoside (DP) is a bioactive compound of Hibiscus sabdariffa L. (Malvaceae) (Roselle) calyces and exerts endothelial protection and lipid-lowering activities, which provided a basis for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Objectives: To investigate the therapeutic effects of DP against atherosclerosis.
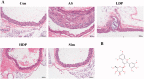
Materials and methods: A rabbit model of atherosclerosis (AS) was established by 12 weeks of a high-fat diet (HFD). The rabbits were divided into five groups: control, AS, simvastatin (4 mg/kg), and two DP groups (10 and 20 mg/kg). After treatment with DP or simvastatin by oral gavage for 12 weeks, the lipid profiles were measured. Histopathological assessment of the aorta was performed by H&E staining. Oxidative stress and inflammation-related markers were analyzed by ELISA kit and real-time RT-PCR.
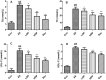
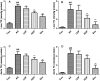
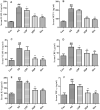
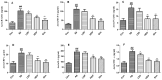
Results: DP (20 mg/kg) decreased serum TG (2.36 ± 0.66 vs. 4.33 ± 0.27 mmol/L for the AS group), TC, LDL-C, and HDL-C (all p < 0.05). DP (20 mg/kg) also reduced lipid levels in the liver and aorta. DP (20 mg/kg) down-regulated the mRNA levels of IL-6, VCAM-1, and NF-κB and up-regulated the mRNA levels of GSH-PX and SOD1.
Conclusions: This study proved that DP alleviated the HFD-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in atherosclerosis rabbits. These results provided the scientific basis for developing novel therapies.
Keywords: Hypolipidemic effect; antioxidant effect; high-fat diet; inflammatory cytokines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
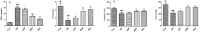
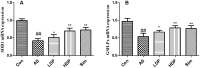
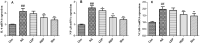
Similar articles
-
Delphinidin-3-sambubioside from Hibiscus sabdariffa. L attenuates hyperlipidemia in high fat diet-induced obese rats and oleic acid-induced steatosis in HepG2 cells.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):3837-3849. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1950259. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34281481 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory activity and molecular mechanism of delphinidin 3-sambubioside, a Hibiscus anthocyanin.Biofactors. 2015 Jan-Feb;41(1):58-65. doi: 10.1002/biof.1201. Biofactors. 2015. PMID: 25728636
-
Inflammation inhibition and gut microbiota regulation by TSG to combat atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Jan 30;247:112232. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112232. Epub 2019 Oct 10. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31606534
-
[Therapeutic potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa: a review of the scientific evidence].Endocrinol Nutr. 2014 May;61(5):274-95. doi: 10.1016/j.endonu.2013.10.012. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Endocrinol Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24444676 Review. Spanish.
-
A review on phytochemistry and therapeutic uses of Hibiscus sabdariffa L.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jun;102:575-586. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.023. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29597091 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Role of Dietary Phenolic Compounds in the Prevention and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current Reports.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 6;17(5):590. doi: 10.3390/ph17050590. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial effects of flavonoids on animal models of atherosclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis.iScience. 2023 Oct 27;26(11):108337. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108337. eCollection 2023 Nov 17. iScience. 2023. PMID: 38026172 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPRi knockdown of mycobacterial tkt gene potentiates the anti-mycobacterial activity of phyto-compounds from selected medicinal plants.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04987-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40615820 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemistry of Antioxidants: Mechanisms and Pharmaceutical Applications.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 25;10(12):3051. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123051. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Hibiscus sabdariffa Linn. in Attenuating Cardiovascular Risk Factors.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 May 29;16(6):807. doi: 10.3390/ph16060807. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375755 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen CC, Hsu JD, Wang SF, Chiang HC, Yang MY, Kao ES, Ho YC, Wang CJ.. 2003. Hibiscus sabdariffa extract inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits. J Agric Food Chem. 51(18):5472–5477. - PubMed
-
- Dayoub O, Le Lay S, Soleti R, Clere N, Hilairet G, Dubois S, Gagnadoux F, Boursier J, Martínez MC, Andriantsitohaina R.. 2017. Estrogen receptor α/HDAC/NFAT axis for delphinidin effects on proliferation and differentiation of T lymphocytes from patients with cardiovascular risks. Sci Rep. 7(1):9378. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garcia C, Blesso CN.. 2021. Antioxidant properties of anthocyanins and their mechanism of action in atherosclerosis. Free Radic Biol Med. 172:152–166. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
