Plasma apolipoprotein concentrations and incident diabetes in subjects with prediabetes
- PMID: 35130909
- PMCID: PMC8822824
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-022-01452-5
Plasma apolipoprotein concentrations and incident diabetes in subjects with prediabetes
Abstract
Background: The identification of circulating biomarkers associated with the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) is useful for improving the current prevention strategies in the most at-risk patients. Here, we aimed to investigate the association of plasma apolipoprotein concentrations in prediabetes subjects with the incidence of new-onset T2D during follow-up.
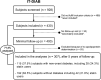
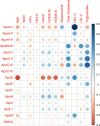
Methods: In the IT-DIAB prospective study, 307 participants with impaired fasting glucose levels (fasting plasma glucose [FPG]: 110-125 mg/dL) were followed yearly for 5 years. The onset of T2D was defined as a first FPG value ≥ 126 mg/dL during follow-up. Apolipoprotein (apo)A-I, A-II, A-IV, B100, C-I, C-II, C-III, C-IV, D, E, F, H, J, L1, M, and (a) plasma concentrations were determined by mass spectrometry. Correlations between apolipoproteins and metabolic parameters at baseline were assessed by Spearman's coefficients. Kaplan-Meier curves were drawn using a ternary approach based on terciles and incident T2D. The association between plasma apolipoproteins concentrations and the incidence of T2D was determined using Cox proportional-hazards models.
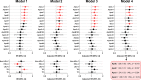
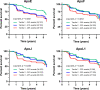
Results: During a median follow-up of 5-year, 115 participants (37.5%) developed T2D. After adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, FPG, HbA1c, and statin use, the plasma levels of apoC-I, apoC-II, apoC-III, apoE, apoF, apoH, apoJ, and apoL1 were positively associated with a high risk for T2D. After further adjustment for plasma triglycerides, only apoE (1 SD natural-log-transformed hazard ratio: 1.28 [95% confidence interval: 1.06; 1.54]; p = 0.010), apoF (1.22 [1.01; 1.48]; p = 0.037), apoJ (1.24 [1.03; 1.49]; p = 0.024), and apoL1 (1.26 [1.05; 1.52]; p = 0.014) remained significantly associated with the onset of T2D. Kaplan-Meier survival curves also showed that the lower third of plasma apoE levels (< 5.97 mg/dL) was significantly associated with a lower risk of conversion to T2D (log-rank test, p = 0.002) compared to the middle and upper thirds.
Conclusions: The plasma apoE levels are positively associated with the risk of T2D in prediabetes subjects, independently of traditional risk factors. The possible associations of apoF, apoJ, and apoL1 with T2D risk also pave the way for further investigations. Trial registration This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT01218061 and NCT01432509.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein E; Apolipoproteins; IT-Diab study; New-onset diabetes; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There are no competing interests related to this work to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;157:107843. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ. The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus–present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;8:228–236. - PubMed
-
- Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 2013;93:137–188. - PubMed
-
- Ferreira JP, Lamiral Z, Xhaard C, Duarte K, Bresso E, Devignes M-D, et al. Circulating plasma proteins and new-onset diabetes in a population-based study: proteomic and genomic insights from the STANISLAS cohort. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020;183:285–295. - PubMed
-
- Athyros VG, Doumas M, Imprialos KP, Stavropoulos K, Georgianou E, Katsimardou A, et al. Diabetes and lipid metabolism. Horm Athens Greece. 2018;17:61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

