Spatial context and the functional role of the postrhinal cortex
- PMID: 35131453
- PMCID: PMC8897231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2022.107596
Spatial context and the functional role of the postrhinal cortex
Abstract
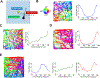
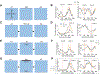
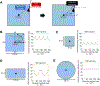
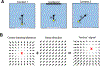
The postrhinal cortex (POR) serves as a key input area to the hippocampal system. It receives highly processed information from the ventral visual stream and other limbic areas including the retrosplenial cortex, parahippocampal areas, and portions of the limbic thalamus. The POR was studied early on by David Bucci and colleagues who first postulated that the POR plays a major role in contextual learning. Here we review a number of approaches and experimental studies that have explored POR's role in contextual processing. We discuss POR lesion studies that monitored deficits in fear conditioning tasks and the effects that these lesions had on processing visual landmark information. We then review the types of spatial correlates encoded by POR cells. A large number of head direction (HD) cells are present, although recent findings suggest that many of them are more accurately characterized as landmark modulated-HD cells as opposed to classic HD cells. A significant number of POR cells are also tuned to egocentric properties of the environment, such as the spatial relationship of the animal to the center of its environment, or the distance between the animal and either the environment's center or its boundaries. We suggest potential frameworks through which these functional cell types might support contextual processing. We then discuss deficits seen in humans who have damage to the homologous parahippocampal cortex, and we finish by reviewing functional imaging studies that found activation of this area while human subjects performed various tasks. A preponderance of evidence suggests that the POR, along with its interactions with retrosplenial cortex, plays a key role in contextual information processing.
Keywords: Context; Egocentric; Postrhinal cortex; Spatial orientation; Visual landmarks.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The postrhinal cortex is not necessary for landmark control in rat head direction cells.Hippocampus. 2017 Feb;27(2):156-168. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22680. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Hippocampus. 2017. PMID: 27860052 Free PMC article.
-
Corticohippocampal contributions to spatial and contextual learning.J Neurosci. 2004 Apr 14;24(15):3826-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0410-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15084664 Free PMC article.
-
Disconnection of the Perirhinal and Postrhinal Cortices Impairs Recognition of Objects in Context But Not Contextual Fear Conditioning.J Neurosci. 2017 May 3;37(18):4819-4829. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0254-17.2017. Epub 2017 Apr 14. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28411272 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a conceptualization of retrohippocampal contributions to learning and memory.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014 Dec;116:197-207. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 27. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2014. PMID: 24878277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the hippocampus: The role of parahippocampal-prefrontal communication in context-modulated behavior.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021 Nov;185:107520. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107520. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2021. PMID: 34537379 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Geometric determinants of the postrhinal egocentric spatial map.Curr Biol. 2023 May 8;33(9):1728-1743.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2023.03.066. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Curr Biol. 2023. PMID: 37075750 Free PMC article.
-
cFOS as a biomarker of activity maturation in the hippocampal formation.Front Neurosci. 2023 Jul 13;17:929461. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.929461. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37521697 Free PMC article.
-
Using multi-task experiments to test principles of hippocampal function.Hippocampus. 2023 May;33(5):646-657. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23540. Epub 2023 Apr 12. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 37042212 Free PMC article.
-
The Anterior Thalamus Preferentially Drives Allocentric But Not Egocentric Orientation Tuning in Postrhinal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2024 Mar 6;44(10):e0861232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0861-23.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38286624 Free PMC article.
-
Scene Perception and Visuospatial Memory Converge at the Anterior Edge of Visually Responsive Cortex.J Neurosci. 2023 Aug 2;43(31):5723-5737. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2043-22.2023. Epub 2023 Jul 20. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37474310 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguirre GK, Ketre JA, Alsop DC, & D’Esposito M (1996). The parahippocampus subserves topographical learning in man. Cerebral Cortex 6, 823–829. - PubMed
-
- Barrash J, Damasio H, Adolphs R, & Tranel D (2000). The neuroanatomical correlates of route learning impairment. Neuropsychologia 38, 820–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

