Evidence of vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and interstitial pneumonia in second-trimester twin stillbirth in asymptomatic woman. Case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 35131495
- PMCID: PMC8815276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2022.100589
Evidence of vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and interstitial pneumonia in second-trimester twin stillbirth in asymptomatic woman. Case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Data on the vertical transmission rate of COVID-19 in pregnancy are limited, although data reporting mother-fetal transmission in the second trimester of pregnancy are controversial. We described a case of second-trimester twin stillbirth in a woman with SARS-CoV-2 infection in which placental and fetal markers of infection were detected, despite the absence of respiratory syndrome. The patient developed clinical chorioamnionitis and spontaneously delivered 2 stillborn infants. Placental histology and immunohistochemistry demonstrated SARS-CoV-2 infection mostly within the syncytiotrophoblast, and fetal autopsy showed the development of interstitial pneumonia. Our findings demonstrated that in utero vertical transmission is possible in asymptomatic pregnant women with SARS-CoV-2 infection and that infection can lead to severe morbidity in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
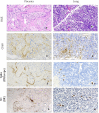
References
-
- Goh XL, Low YF, Ng CH, Amin Z, Ng YPM. Incidence of SARS-CoV-2 vertical transmission: a meta-analysis. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2021;106:112–113. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DA, Baldewijns M, Benachi A, et al. Chronic histiocytic intervillositis with trophoblast necrosis is a risk factor associated with placental infection from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and intrauterine maternal-fetal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) transmission in live-born and stillborn infants. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021;145:517–528. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz DA, Levitan D. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infecting pregnant women and the fetus, intrauterine transmission, and placental pathology during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: it's complicated. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021;145:925–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

