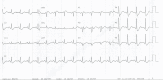
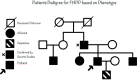
Refractory familial hypokalaemic periodic paralysis leading to cardiovascular compromise
- PMID: 35131788
- PMCID: PMC8823031
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2021-246674
Refractory familial hypokalaemic periodic paralysis leading to cardiovascular compromise
Abstract
Familial hypokalaemic periodic paralysis (FHPP) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that is classified under periodic paralysis (PP), which is characterised by episodes of muscle weakness. Common triggers include intense exercise, fasting or consumption of carbohydrate-rich meals. Hypokalaemic PP has an incidence of 1 in 100 000; despite the temporal association, cardiac manifestations are exceedingly rare. We present a case of FHPP, a channelopathy presenting with severe refractory hypokalaemia. The challenges with our patient were maintaining potassium levels within normal ranges and initiating a close follow-up plan. Due to the lack of clinical guidance in our case, many aspects of care, including surveillance, medications and genetic testing, remain unaddressed. Medical management includes aggressive correction with supplements, potassium-sparing diuretics and carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Severe cases of dysrhythmias, especially ventricular fibrillation, require electrophysiology evaluation and possible implantation of a defibrillator to prevent sudden cardiac death.
Keywords: adult intensive care; arrhythmias; fluid electrolyte and acid-base disturbances; metabolic disorders; pacing and electrophysiology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2022. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Loh KC, Pinheiro L, Ng KS,. Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis complicated by near-fatal ventricular arrhythmias. Singapore Med J 2005;46:88. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous