Use and Outcomes of Induction Therapy in Well-Matched Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 35131930
- PMCID: PMC8823946
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.09170721
Use and Outcomes of Induction Therapy in Well-Matched Kidney Transplant Recipients
Erratum in
-
Correction: Use and Outcomes of Induction Therapy in Well-Matched Kidney Transplant Recipients.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Dec;17(12):1802-1804. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10870922. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36220191 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and objectives: The optimal induction treatment in low-immune risk kidney transplant recipients is uncertain. We therefore investigated the use and outcomes of induction immunosuppression in a low-risk cohort of patients who were well matched with their donor at HLA-A, -B, -DR, -DQB1 on the basis of serologic typing.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Our study was an observational study of first adult kidney-only transplant recipients in the United States recorded by the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network.
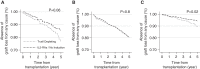
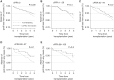
Results: Among 2976 recipients, 57% were treated with T cell-depleting antibodies, 28% were treated with an IL-2 receptor antagonist, and 15% were treated without induction. There was no difference in allograft survival, death-censored graft survival, or death with function between patients treated with an IL-2 receptor antagonist and no induction therapy. In multivariable models, patients treated with T cell-depleting therapy had a similar risk of graft loss from any cause, including death (hazard ratio, 1.19; 95% confidence interval, 0.98 to 1.45), compared with patients treated with an IL-2 receptor antagonist or no induction. The findings were consistent in subgroup analyses of Black recipients, patients grouped by calculated panel reactive antibody, and donor source. The incidence of acute rejection at 1 year was low (≤5%) and did not vary between treatment groups.
Conclusions: Use of induction therapy with T cell-depleting therapy or IL-2 receptor antagonists in first kidney transplant recipients who are well matched with their donor at the HLA-A, -B, -DR, -DQB1 gene loci is not associated with improved post-transplant outcomes.
Keywords: United States Renal Data System; acute rejection; immunosuppression; kidney transplantation; organ transplant.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Induction Therapy in Immunologically Well-Matched Recipients: Less May Be More.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022 Feb;17(2):173-175. doi: 10.2215/CJN.16591221. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 35131923 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Transplant Work Group : KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the care of kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant 9[Suppl 3]: S1–S155, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Gebel HM, Bray RA, Nickerson P: Pre-transplant assessment of donor-reactive, HLA-specific antibodies in renal transplantation: Contraindication vs. risk. Am J Transplant 3: 1488–1500, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Pei R, Lee J-H, Shih N-J, Chen M, Terasaki PI: Single human leukocyte antigen flow cytometry beads for accurate identification of human leukocyte antigen antibody specificities. Transplantation 75: 43–49, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Cecka JM: Calculated PRA (CPRA): The new measure of sensitization for transplant candidates. Am J Transplant 10: 26–29, 2010 - PubMed
-
- Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Bragg-Gresham J, Chen X, Gipson D, Gu H, Hirth RA, Hutton D, Jin Y, Kapke A, Kurtz V, Li Y, McCullough K, Modi Z, Morgenstern H, Mukhopadhyay P, Pearson J, Pisoni R, Repeck K, Schaubel DE, Shamraj R, Steffick D, Turf M, Woodside KJ, Xiang J, Yin M, Zhang X, Shahinian V: US Renal Data System 2019 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 75[Suppl 1]: A6–A7, 2020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

