Enhanced germline stem cell longevity in Drosophila diapause
- PMID: 35132083
- PMCID: PMC8821637
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28347-z
Enhanced germline stem cell longevity in Drosophila diapause
Abstract
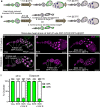
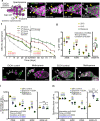
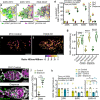
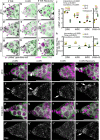
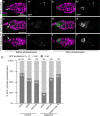
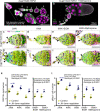
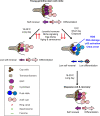
In many species including humans, aging reduces female fertility. Intriguingly, some animals preserve fertility longer under specific environmental conditions. For example, at low temperature and short day-length, Drosophila melanogaster enters a state called adult reproductive diapause. As in other stressful conditions, ovarian development arrests at the yolk uptake checkpoint; however, mechanisms underlying fertility preservation and post-diapause recovery are largely unknown. Here, we report that diapause causes more complete arrest than other stresses yet preserves greater recovery potential. During dormancy, germline stem cells (GSCs) incur DNA damage, activate p53 and Chk2, and divide less. Despite reduced niche signaling, germline precursor cells do not differentiate. GSCs adopt an atypical, suspended state connected to their daughters. Post-diapause recovery of niche signaling and resumption of division contribute to restoring GSCs. Mimicking one feature of quiescence, reduced juvenile hormone production, enhanced GSC longevity in non-diapausing flies. Thus, diapause mechanisms provide approaches to GSC longevity enhancement.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Reynolds JA. Noncoding RNA regulation of dormant states in evolutionarily diverse animals. Biol. Bull. 2019;237:192–209. - PubMed
-
- Tougeron K. Diapause research in insects: historical review and recent work perspectives. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2019;167:27–36.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

