Interface engineering of Ta3N5 thin film photoanode for highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting
- PMID: 35132086
- PMCID: PMC8821563
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28415-4
Interface engineering of Ta3N5 thin film photoanode for highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting
Abstract
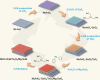
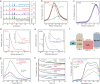
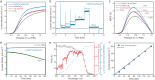
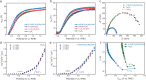
Interface engineering is a proven strategy to improve the efficiency of thin film semiconductor based solar energy conversion devices. Ta3N5 thin film photoanode is a promising candidate for photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting. Yet, a concerted effort to engineer both the bottom and top interfaces of Ta3N5 thin film photoanode is still lacking. Here, we employ n-type In:GaN and p-type Mg:GaN to modify the bottom and top interfaces of Ta3N5 thin film photoanode, respectively. The obtained In:GaN/Ta3N5/Mg:GaN heterojunction photoanode shows enhanced bulk carrier separation capability and better injection efficiency at photoanode/electrolyte interface, which lead to a record-high applied bias photon-to-current efficiency of 3.46% for Ta3N5-based photoanode. Furthermore, the roles of the In:GaN and Mg:GaN layers are distinguished through mechanistic studies. While the In:GaN layer contributes mainly to the enhanced bulk charge separation efficiency, the Mg:GaN layer improves the surface charge inject efficiency. This work demonstrates the crucial role of proper interface engineering for thin film-based photoanode in achieving efficient PEC water splitting.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hu S, et al. Amorphous TiO2 coatings stabilize Si, GaAs, and GaP photoanodes for efficient water oxidation. Science. 2014;344:1005–1009. - PubMed
-
- Takata T, et al. Photocatalytic water splitting with quantum efficiency of almost unity. Nature. 2020;581:411–414. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, et al. Scalable water splitting on particulate photocatalyst sheets with a solar-to-hydrogen energy conversion efficiency exceeding 1% Nat. Mater. 2016;15:611–615. - PubMed
-
- Nishiyama H, et al. Photocatalytic solar hydrogen production from water on a 100 m2-scale. Nature. 2021;598:304–307. - PubMed
-
- Lewis NS. Toward cost-effective solar energy use. Science. 2007;315:798–801. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- ARPChem/New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)
- ARPChem/New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)
- ARPChem/New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)
- JPMXP09-A-20-UT-0004/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
- JPMXP09-A-20-UT-0004/Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

