Diagnostic performance of core needle biopsy for nodal recurrences in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35132145
- PMCID: PMC8821564
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06102-0
Diagnostic performance of core needle biopsy for nodal recurrences in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
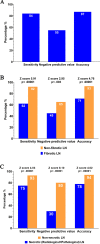
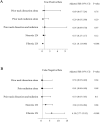
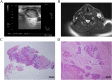
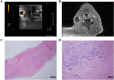
This study investigated the diagnostic accuracy and affecting factors of ultrasound (US)-guided core-needle biopsy (CNB) in patients with treated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). We retrospectively reviewed patients with treated HNSCC who received US-guided CNB from January 2011 to December 2018 with corresponding imaging. Pathological necrosis and fibrosis of targeted lymph nodes (LNs) were evaluated. We analyzed the correlation between CNB accuracy and clinical and pathological characteristics. In total, 260 patients were included. The overall sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of CNB for nodal recurrence were 84.47%, 100%, 100%, 54.67%, and 86.92%, respectively. CNB of fibrotic LNs had significantly worse sensitivity, NPV, and accuracy than that of non-fibrotic LNs. Similarly, CNB of necrotic LNs had significantly worse sensitivity, NPV, and accuracy than non-necrotic LNs. Multivariate regression revealed that fibrotic LN was the only independent factor for a true positive rate, whereas both necrotic LN and fibrotic LN were independent factors for a false negative rate. The diagnostic accuracy of CNB in treated HNSCC patients is affected by LN necrosis and fibrosis. Therefore, CNB results, particularly for necrotic or fibrotic LNs, should be interpreted carefully.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Applications and Potential Developments of Ultrasound in Oral Cancer Management.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221133216. doi: 10.1177/15330338221133216. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 36254559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The application of ultrasound in detecting lymph nodal recurrence in the treated neck of head and neck cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2017 Jun 21;7(1):3958. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04039-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28638103 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of sentinel lymph node biopsy by ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy for patients with suspicious node positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer. 2018 Jan;25(1):86-93. doi: 10.1007/s12282-017-0795-7. Epub 2017 Jul 22. Breast Cancer. 2018. PMID: 28735457
-
Efficacy of ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy in cervical lymphadenopathy: A retrospective study of 6,695 cases.Eur Radiol. 2018 May;28(5):1809-1817. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-5116-1. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29188372
-
Diagnostic value and accuracy of imprint cytology evaluation during image-guided core needle biopsies: Review of our experience at a large academic center.Diagn Cytopathol. 2015 Oct;43(10):773-9. doi: 10.1002/dc.23300. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Diagn Cytopathol. 2015. PMID: 26119885 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Cell-free DNA as a Non-Invasive Biomarker in the Detection of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2025 Apr;40(2):294-299. doi: 10.1007/s12291-024-01181-4. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40123626
-
A Narrative Review of the Role of Non-Viral Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling in Predicting the Treatment Response and Recurrence in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 9;17(14):2279. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142279. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Applications and Potential Developments of Ultrasound in Oral Cancer Management.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Jan-Dec;21:15330338221133216. doi: 10.1177/15330338221133216. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 36254559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

