Single-center prospective study on the efficacy of nivolumab against platinum-sensitive recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35132165
- PMCID: PMC8821556
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-06084-z
Single-center prospective study on the efficacy of nivolumab against platinum-sensitive recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
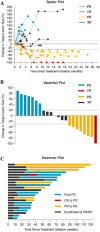
Nivolumab, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, is beneficial to patients with platinum-refractory recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (R/M-HNSCC). However, platinum-sensitive R/M-HNSCC has not yet been studied. Hence, in this prospective study, we evaluated the efficacy and safety of nivolumab in patients with platinum-sensitive R/M-HNSCC. This prospective single-arm study was conducted in a single institution in Japan. Patients with platinum-sensitive R/M-HNSCC (defined as head and neck cancer that recurred or metastasized at least 6 months after platinum-based chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy) were enrolled. The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS). The secondary endpoints were progression-free survival (PFS), overall response rate (ORR), immune-related adverse events (irAEs), and quality of life (QOL). This study was registered at the University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry (UMIN000031324). Twenty-two patients with platinum-sensitive R/M-HNSCC were enrolled. The median OS was 17.4 months, and the 1-year OS rate was 73%. The median PFS was 9.6 months, 1-year PFS rate was 48%, and ORR was 36%. Sixteen irAEs were recorded in 12 patients; however, no grade 4 or 5 irAEs were observed. The QOL assessments revealed that nivolumab did not decrease the QOL of patients. Nivolumab is effective against platinum-sensitive R/M-HNSCC with acceptable safety.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Wiegand S, Zimmermann A, Wilhelm T, Werner JA. Survival after distant metastasis in head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015;35:5499–5502. - PubMed
-
- Dang RP, et al. Clinical outcomes in patients with recurrent or metastatic human papilloma virus-positive head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016;36:1703–1709. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

