Liquid BIOpsy for MiNimal RESidual DiSease Detection in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (LIONESS)-a personalised circulating tumour DNA analysis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35132238
- PMCID: PMC9023460
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-022-01716-7
Liquid BIOpsy for MiNimal RESidual DiSease Detection in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (LIONESS)-a personalised circulating tumour DNA analysis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remain a substantial burden to global health. Cell-free circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA) is an emerging biomarker but has not been studied sufficiently in HNSCC.
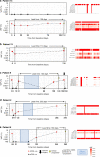
Methods: We conducted a single-centre prospective cohort study to investigate ctDNA in patients with p16-negative HNSCC who received curative-intent primary surgical treatment. Whole-exome sequencing was performed on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumour tissue. We utilised RaDaRTM, a highly sensitive personalised assay using deep sequencing for tumour-specific variants, to analyse serial pre- and post-operative plasma samples for evidence of minimal residual disease and recurrence.
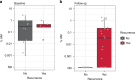
Results: In 17 patients analysed, personalised panels were designed to detect 34 to 52 somatic variants. Data show ctDNA detection in baseline samples taken prior to surgery in 17 of 17 patients. In post-surgery samples, ctDNA could be detected at levels as low as 0.0006% variant allele frequency. In all cases with clinical recurrence to date, ctDNA was detected prior to progression, with lead times ranging from 108 to 253 days.
Conclusions: This study illustrates the potential of ctDNA as a biomarker for detecting minimal residual disease and recurrence in HNSCC and demonstrates the feasibility of personalised ctDNA assays for the detection of disease prior to clinical recurrence.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SF, PB, CR, MC, OG and CW declare no competing interests. KH, SH, CP, KM, PE, TF and GM are employees and shareholders of Inivata Ltd (Cambridge, UK).
Figures


References
-
- Cohen N, Fedewa S, Chen AY. Epidemiology and demographics of the head and neck cancer population. Oral Maxillofacial Surg Clin North Am. 2018;30:381–95. - PubMed
-
- Machiels J-P, Leemans CR, Golusinski W, Grau C, Licitra L, Gregoire V, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity, larynx, oropharynx and hypopharynx: EHNS–ESMO–ESTRO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 2020;31:1462–75.. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.07.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

