Effects of the Chinese Herb Medicine Formula "She-Xiang-Yu-Hong" Ointment on Wound Healing Promotion in Diabetic Mice
- PMID: 35132324
- PMCID: PMC8817837
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1062261
Effects of the Chinese Herb Medicine Formula "She-Xiang-Yu-Hong" Ointment on Wound Healing Promotion in Diabetic Mice
Abstract
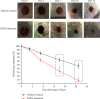
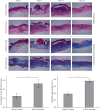
Wound healing in diabetic patients is a difficult problem to be solved at present. In addition, patients with diabetes have an increased risk of postoperative wound complications. "She-Xiang-Yu-Hong" (SXYH) ointment is a type of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) compound used to treat wounds. Over the past few years, SXYH has been applied in the Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University of TCM (Chengdu, China) for the treatment of diabetic foot infections and bedsores, whereas there has been rare research on the effect of SXYH ointment on wound healing. In this study, SXYH ointment was first applied to streptozotocin (STZ)-triggered diabetic ICR mice (4-6 weeks, 20 ± 2 g) to observe the accelerated wound healing and the shortened wound healing period. As indicated by the histology and biochemistry analyses of skin biopsies, the wounds treated using SXYH ointment showed an increase in the granulation tissue. Moreover, SXYH also modulated the inflammation response by regulating affinity proinflammatory cytokines release (e.g., IL-6 and TNF-α). Furthermore, SXYH ointment obviously improved collagen fiber deposition and tissue on the wound surface. On the whole, this study indicated that SXYH ointment could accelerate wound healing, promote blood vessel formation, and suppress inflammations. Thus, the clinical potential of SXYH ointment was demonstrated in the treatment of diabetes and refractory wounds.
Copyright © 2022 Qingjie Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paris polyphylla Sm. characterized extract infused ointment accelerates diabetic wound healing in In-vivo model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Sep 15;331:118296. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118296. Epub 2024 May 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38710458
-
Effects of the Four-Herb Compound ANBP on Wound Healing Promotion in Diabetic Mice.Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015 Dec;14(4):335-42. doi: 10.1177/1534734615575244. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2015. PMID: 25795279
-
[Effects of Huanglian ointment on wound healing of mice with full-thickness skin defect and the related mechanism].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 20;32(12):714-720. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2016.12.003. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28043294 Chinese.
-
The signaling pathways of traditional Chinese medicine in promoting diabetic wound healing.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;282:114662. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114662. Epub 2021 Sep 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34555452 Review.
-
[Research progress in role of autophagy in diabetic wound healing and traditional Chinese medicine intervention].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Apr;48(7):1724-1730. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20221219.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37282946 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Advances in the Preparation of Nanofiber Dressings by Electrospinning for Promoting Diabetic Wound Healing.Biomolecules. 2022 Nov 22;12(12):1727. doi: 10.3390/biom12121727. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Difficulties in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot and Research Progress of Combination of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 11;2022:9449427. doi: 10.1155/2022/9449427. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9807270. doi: 10.1155/2023/9807270. PMID: 35991142 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
An Overview of Wound Dressing Materials.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;17(9):1110. doi: 10.3390/ph17091110. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shiffman M., Low M. Chronic Wounds, Wound Dressings and Wound Healing . Berlin, Germany: Springer; 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

