Serum-Based lncRNA ANRIL, TUG1, UCA1, and HIT Expressions in Breast Cancer Patients
- PMID: 35132340
- PMCID: PMC8817891
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9997212
Serum-Based lncRNA ANRIL, TUG1, UCA1, and HIT Expressions in Breast Cancer Patients
Abstract
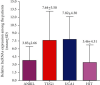
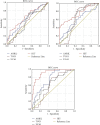
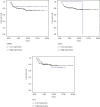
Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease and is the most common and prevalent form of malignancy diagnosed in women. lncRNAs are found to be frequently dysregulated in cancer, and its expression plays a critical role in tumorigenesis. The study included 100 histopathologically confirmed, newly diagnosed untreated patients of invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) of breast cancer patients and 100 healthy subjects. After blood collection, the serum was separated and total RNA was extracted, cDNA was synthesized using 100 ng of total RNA, and lncRNA (ANRIL, TUG1, UCA1, and HIT) expression was analyzed. Increased ANRIL (3.83-fold), TUG1 (7.64-fold), UCA1 (7.82-fold), and HIT (3.31-fold) expressions were observed in breast cancer patients compared to healthy controls. Relative expression of lncRNAs UCA-1 (p = 0.010) and HIT-1 (p < 0.0001) was significantly elevated in patients with advanced breast cancer stage compared to those with early-stage disease. While lncRNA TUG-1 expression was found to be higher in patients with early-stage tumors than those with advanced-stage tumors (p = 0.06), lncRNA ANRIL showed increased expression in patients with PR positive status (p = 0.04). However, we found a significant difference in lncRNA HIT expression in HER-2 positive breast cancer patients compared to HER-2 negative breast cancer patients (p = 0.005). An increase in the expression of serum lncRNAs ANRIL (p < 0.0001), UCA-1 (p = 0.004), and HIT (p < 0.0001) was observed in the distant organ metastatic breast cancer patients. In the ROC curve concerning lymph node involvement, the sensitivity and specificity of lncRNA HIT were 68% and 58%, respectively (p value = 0.007). In the ROC curve w.r.t. stages of disease, the sensitivity and specificity of lncRNA HIT were 80% and 50%, respectively (p value < 0.0001). Better sensitivity and specificity were observed for lncRNA HIT (sensitivity 91% and specificity 78%; p value < 0.0001) and ANRIL (sensitivity 70% and specificity 60%; p value < 0.0001) w.r.t distant organ metastases.
Copyright © 2022 Ali G. Alkhathami et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNAs antisense noncoding RNA in the INK4 locus (ANRIL) correlates with lower acute exacerbation risk, decreased inflammatory cytokines, and mild GOLD stage in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.J Clin Lab Anal. 2019 Feb;33(2):e22678. doi: 10.1002/jcla.22678. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Clin Lab Anal. 2019. PMID: 30230590 Free PMC article.
-
Increased expression of the long non-coding RNA ANRIL promotes lung cancer cell metastasis and correlates with poor prognosis.Diagn Pathol. 2015 Mar 27;10:14. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0247-7. Diagn Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25889788 Free PMC article.
-
Serum LncRNA-ATB and FAM83H-AS1 as diagnostic/prognostic non-invasive biomarkers for breast cancer.Life Sci. 2020 Oct 15;259:118193. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118193. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32763293
-
Long noncoding RNA ANRIL: a potential novel prognostic marker in cancer: a meta-analysis.Minerva Med. 2016 Apr;107(2):77-83. Minerva Med. 2016. PMID: 27176569 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNAs: From disease code to drug role.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Feb;11(2):340-354. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33643816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic association of long non-coding RNA ANRIL polymorphism with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Chinese Han population.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025 Mar 28;17(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01670-3. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2025. PMID: 40148977 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 20;15(3):454. doi: 10.3390/biom15030454. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Urothelial Cancer-Associated 1 in Gynecological Cancers.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 21;46(3):2772-2797. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030174. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal LncRNAs in Gastrointestinal Cancer: Biological Functions and Emerging Clinical Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 2;15(3):959. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030959. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oncogenic Dysregulation of Circulating Noncoding RNAs: Novel Challenges and Opportunities in Sarcoma Diagnosis and Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 26;14(19):4677. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194677. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230599 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA: a Cancer Journal for Clinicians . 2018;68(1):7–30. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

