The Effect of Ultrasonic Water Treatment on the Change in the Microstructure of Wheat Grain, Dough, and Wheat Flour Bread
- PMID: 35132373
- PMCID: PMC8817881
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1986438
The Effect of Ultrasonic Water Treatment on the Change in the Microstructure of Wheat Grain, Dough, and Wheat Flour Bread
Abstract
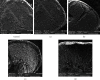
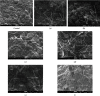
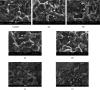
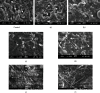
Visualization of the microstructure of the food matrix of both raw materials and the final product is one of the keys to understanding the processes occurring during its formation. It is the fixation of the results at the microlevel that allows us to form a hypothesis and then confirm it with the obtained array of experimental data. The presented study is aimed at studying the effect of ultrasonic water treatment on the change in the microstructure of wheat grain during its humidification. The article also presents the results of studying the microstructure of dough and wheat flour bread obtained using water after ultrasonic water treatment and the intensity of the processes of staling of finished bread in storage. The object of the study was grain of soft spring white wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), varieties of Lubava, harvest 2014-2018, Russia (the protein content was 12.5 ± 0.3 g/100 g in terms of humidity); dough and bread made from wheat flour (ash content 0.55%, mass fraction of gluten 28.5%), produced using the technology of plain bread, a classic recipe without improvers. Ultrasound-treated water with an exposure frequency of 22 ± 1.65 kHz and with a power variation of 252-630 W/l was used in test technology. The experimental data obtained made it possible to establish the intensification of the processes of swelling of wheat grain during soaking. In the experimental samples, after 8 hours of soaking, the loosened structure of the endosperm and evenly swollen components of the grain were observed, and the loop of the groove was closed. Activation of the processes of dough science was established, and gluten flour in the dough formed a single monolithic frame, in which the swollen starch grains are tightly packed. The interstitial walls of the crumb of the prototypes consisted of a solid mass of protein coagulated during baking, inside of which swollen gelatinized starch grains are interspersed, they are closely adjacent to the mass of coagulated protein with their entire surface, and therefore, there is no sharp, clearly visible boundary between them. The most pronounced changes in the structure of the dough and bread crumb were noted when using water, after ultrasonic water treatment at a power of 504 and 630 W/l. This method of exposure can be recommended as the best for obtaining good quality bread with less pronounced staling during storage.
Copyright © 2022 Natalia Naumenko et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Naumenko N. V., Kalinina I. V. Sonochemistry effects influence on the adjustments of raw materials and finished goods properties in food production, International. Conference on Industrial Engineering; 19-20 May 2016; Chelyabinsk; Russian Federation 870. pp. 691–696.
-
- Nilova L., Naumenko N., Kalinina I. A study of the forms of bound water in bread and bakery products using differential thermal analysis. Agronomy Research . 2017;15(S2):1386–1398.
-
- Indrani D., Swetha P., Soumya C., Rajiv J., Rao G. V. Effect of multigrains on rheological, microstructural and quality characteristics of north Indian parotta - an Indian flat bread. LWT- Food Science and Technology . 2011;44(3):719–724. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2010.11.017. - DOI
-
- Barcenas M. E., Rosell C. M. Effect of HPMC addition on the microstructure, quality and aging of wheat bread. Food Hydrocolloids . 2005;19(6):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2005.01.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

