CoviLearn: A Machine Learning Integrated Smart X-Ray Device in Healthcare Cyber-Physical System for Automatic Initial Screening of COVID-19
- PMID: 35132394
- PMCID: PMC8811348
- DOI: 10.1007/s42979-022-01035-x
CoviLearn: A Machine Learning Integrated Smart X-Ray Device in Healthcare Cyber-Physical System for Automatic Initial Screening of COVID-19
Abstract
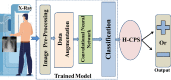
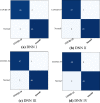
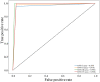
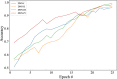
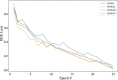
The pandemic of novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) is widespread all over the world causing serious health problems as well as serious impact on the global economy. Reliable and fast testing of the COVID-19 has been a challenge for researchers and healthcare practitioners. In this work, we present a novel machine learning (ML) integrated X-ray device in Healthcare Cyber-Physical System (H-CPS) or smart healthcare framework (called "CoviLearn") to allow healthcare practitioners to perform automatic initial screening of COVID-19 patients. We propose convolutional neural network (CNN) models of X-ray images integrated into an X-ray device for automatic COVID-19 detection. The proposed CoviLearn device will be useful in detecting if a person is COVID-19 positive or negative by considering the chest X-ray image of individuals. CoviLearn will be useful tool doctors to detect potential COVID-19 infections instantaneously without taking more intrusive healthcare data samples, such as saliva and blood. COVID-19 attacks the endothelium tissues that support respiratory tract, and X-rays images can be used to analyze the health of a patient's lungs. As all healthcare centers have X-ray machines, it could be possible to use proposed CoviLearn X-rays to test for COVID-19 without the especial test kits. Our proposed automated analysis system CoviLearn which has 98.98% accuracy will be able to save valuable time of medical professionals as the X-ray machines come with a drawback as it needed a radiology expert.
Keywords: COVID-19; Deep neural network (DNN); Healthcare-Cyber-Physical System (H-CPS); Machine learning; Smart healthcare; X-ray.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Liu T, Hu J, Kang M, Lin L, Zhong H, Xiao J, He G, Song T, Huang Q, Rong Z, Deng A, Zeng W, Tan X, Zeng S, Zhu Z, Li J, Wan D, Lu J, Deng H, He J, Ma W. Transmission dynamics of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-ncov). 2020.
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
