Development of a new ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of digoxin and digitoxin in plasma: Comparison with a clinical immunoassay
- PMID: 35132652
- PMCID: PMC9303718
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.202100290
Development of a new ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the determination of digoxin and digitoxin in plasma: Comparison with a clinical immunoassay
Abstract
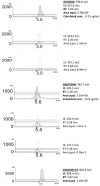
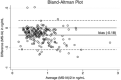
Cardiac glycosides digoxin and digitoxin are used in therapy for the treatment of congestive heart failure. Moreover, these compounds can be responsible for intoxication cases caused by fortuitous ingestion of leaves of Digitalis. Due to the narrow therapeutic range of these drugs, therapeutic drug monitoring is recommended in the clinical practice. In this context, immunoassays-based methods are generally employed but digoxin- and digitoxin-like compounds can interfere with the analysis. The aim of this study was to develop and validate an original UPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of digoxin and digitoxin in plasma. The method shows adequate sensitivity and selectivity with acceptable matrix effects and very good linearity, accuracy, precision, and recovery. A simple liquid-liquid extraction procedure was used for sample clean-up. The method was applied for the analysis of n = 220 plasma samples collected in two different clinical chemistry laboratories and previously tested by the same immunoassay. The statistical comparison showed a relevant negative bias of the UPLC-MS/MS method versus the immunoassay. These results are consistent with an immunoassay overestimation of digoxin plasmatic levels due to cross-reaction events with endogenous digoxin-like substances.
Keywords: Digitoxin; Digoxin; Immunoassay; LC-MS/MS.
© 2022 The Authors. Electrophoresis published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Simultaneous quantification of digoxin, digitoxin, and their metabolites in serum using high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.Drug Test Anal. 2015 Oct;7(10):937-46. doi: 10.1002/dta.1781. Epub 2015 Mar 4. Drug Test Anal. 2015. PMID: 25735870
-
Determination of digoxin and digitoxin in whole blood.J Anal Toxicol. 2009 Sep;33(7):372-8. doi: 10.1093/jat/33.7.372. J Anal Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19796507
-
A novel LC-IDMS/MS method for the determination of the cardiac glycosides digoxin and digitoxin using caesium adducts.Clin Lab. 2006;52(1-2):37-42. Clin Lab. 2006. PMID: 16506362
-
[Analysis of detecting methods of digoxin blood drug level].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007 Feb;32(4):285-8, 326. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 17455457 Review. Chinese.
-
Impact of interferences including metabolite crossreactivity on therapeutic drug monitoring results.Ther Drug Monit. 2012 Oct;34(5):496-506. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0b013e318261c2c9. Ther Drug Monit. 2012. PMID: 22846896 Review.
Cited by
-
Transplacental Therapeutic Drug Monitoring in Pregnant Women with Fetal Tachyarrhythmia Using HPLC-MS/MS.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 17;24(3):1848. doi: 10.3390/ijms24031848. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768172 Free PMC article.
-
A national survey of individualized pharmaceutical care practice in Chinese hospitals in 2019.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1022134. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1022134. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36937844 Free PMC article.
-
Immunosensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Digoxin.ACS Omega. 2023 Apr 17;8(17):15341-15349. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00571. eCollection 2023 May 2. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37151524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whayne, T. F. , Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2018, 18, 427–440. - PubMed
-
- Adams, K. F. , Butler, J. , Patterson, J. H. , Gattis Stough, W. , Bauman, J. L. , van Veldhuisen, D. J. , Schwartz, T. A. , Sabbah, H. , Mackowiak, J. I. , Ventura, H. O. , Ghali, J. K. , Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 1072–1081. - PubMed
-
- Belz, G. G. , Breithaupt‐Grogler, K. , Osowski, U. , Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2001, 31, 10–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

