CXCL12 promotes CCR7 ligand-mediated breast cancer cell invasion and migration toward lymphatic vessels
- PMID: 35133060
- PMCID: PMC8990860
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15293
CXCL12 promotes CCR7 ligand-mediated breast cancer cell invasion and migration toward lymphatic vessels
Abstract
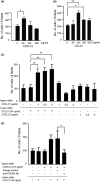
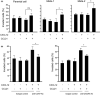
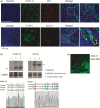
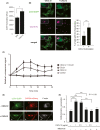
Chemokines are a family of cytokines that mediate leukocyte trafficking and are involved in tumor cell migration, growth, and progression. Although there is emerging evidence that multiple chemokines are expressed in tumor tissues and that each chemokine induces receptor-mediated signaling, their collaboration to regulate tumor invasion and lymph node metastasis has not been fully elucidated. In this study, we examined the effect of CXCL12 on the CCR7-dependent signaling in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells to determine the role of CXCL12 and CCR7 ligand chemokines in breast cancer metastasis to lymph nodes. CXCL12 enhanced the CCR7-dependent in vitro chemotaxis and cell invasion into collagen gels at suboptimal concentrations of CCL21. CXCL12 promoted CCR7 homodimer formation, ligand binding, CCR7 accumulation into membrane ruffles, and cell response at lower concentrations of CCL19. Immunohistochemistry of MDA-MB-231-derived xenograft tumors revealed that CXCL12 is primarily located in the pericellular matrix surrounding tumor cells, whereas the CCR7 ligand, CCL21, mainly associates with LYVE-1+ intratumoral and peritumoral lymphatic vessels. In the three-dimensional tumor invasion model with lymph networks, CXCL12 stimulation facilitates breast cancer cell migration to CCL21-reconstituted lymphatic networks. These results indicate that CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion toward CCR7 ligand-expressing intratumoral lymphatic vessels and supports CCR7 signaling associated with lymph node metastasis.
Keywords: breast cancer; chemokine; invasion; lymph node; metastasis.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemokine axes in breast cancer: factors of the tumor microenvironment reshape the CCR7-driven metastatic spread of luminal-A breast tumors.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):1009-25. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3MA0815-373R. Epub 2016 Mar 2. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26936935
-
The role of CCL21/CCR7 chemokine axis in breast cancer-induced lymphangiogenesis.Mol Cancer. 2015 Feb 10;14:35. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0306-4. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25744065 Free PMC article.
-
Chemokine (C‑C motif) ligand 21/C‑C chemokine receptor type 7 triggers migration and invasion of human lung cancer cells by epithelial‑mesenchymal transition via the extracellular signal‑regulated kinase signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Jun;15(6):4100-4108. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6534. Epub 2017 May 2. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28487957 Free PMC article.
-
Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):869-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0815-380R. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26729814 Review.
-
[Progress in targeting therapy of cancer metastasis by CCL21/CCR7 axis].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Dec 25;36(12):2741-2754. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200174. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33398969 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Implications of inflammatory cell death-related IFNG and co-expressed RNAs (AC006369.1 and CCR7) in breast carcinoma prognosis, and anti-tumor immunity.Front Genet. 2023 Jun 20;14:1112251. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1112251. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37408777 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Dilemma: Metastatic Breast Adenocarcinoma Presenting With a Cholestatic Liver Injury Without Radiological Findings of Liver Metastases.Cureus. 2025 Mar 28;17(3):e81368. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81368. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40291193 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of breast cancer metastatic behavior by microRNAs targeting EMT transcription factors. A relevant participation of miR-196a-5p and miR-22-3p in ZEB1 expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jul;212(2):277-290. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07723-5. Epub 2025 May 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40382762
-
Long-term treatment with benzodiazepines and related Z-drugs exacerbates breast cancer: clinical evidence and molecular mechanisms.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Jun 29;30(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00752-4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40583063 Free PMC article.
-
Reprogramming of sentinel lymph node microenvironment during tumor metastasis.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Oct 20;29(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00868-1. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36266717 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Miyasaka M, Tanaka T. Lymphocyte trafficking across high endothelial venules: dogmas and enigmas. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:360‐370. - PubMed
-
- Ohl L, Mohaupt M, Czeloth N, et al. CCR7 governs skin dendritic cell migration under inflammatory and steady‐state conditions. Immunity. 2004;21:279‐288. - PubMed
-
- Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50‐56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

