Creatine kinase-(MB) and hepcidin as candidate biomarkers for early diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: a proof-of-concept study in Lambaréné, Gabon
- PMID: 35133607
- PMCID: PMC9338130
- DOI: 10.1007/s15010-022-01760-8
Creatine kinase-(MB) and hepcidin as candidate biomarkers for early diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: a proof-of-concept study in Lambaréné, Gabon
Abstract
Background: The present study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic utility of creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), hepcidin (HEPC), phospholipase A2 group IIA (PLa2G2A), and myosin-binding protein C (MYBPC1) for tuberculosis (TB). These four biomarkers are differentially regulated between quiescent Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infected individuals (non-progressors to TB disease) and Mtb-infected TB disease progressors 6 months before the onset of symptoms.
Methods: We enrolled samples from patients experiencing moderate-to-severe pulmonary infections diseases including 23 TB cases confirmed by smear microscopy and culture, and 34 TB-negative cases. For each participant, the serum levels of the four biomarkers were measured using ELISA.
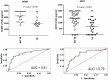
Results: The levels of CK-MB and HEPC were significantly reduced in patients with active TB disease. CK-MB median level was 2045 pg/ml (1455-4000 pg/ml) in active TB cases and 3245 pg/ml (1645-4000 pg/ml) in non-TB pulmonary diseases. Using the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis, HEPC and CK-MB had the Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 79% (95% CI 67-91%) and 81% (95% CI 69-93%), respectively. Both markers correlated with TB diagnosis as a single marker. PLa2G2A and MYBPC1 with AUCs of 48% (95% CI 36-65%) and 62% (95% CI 48-76%) did not performed well as single biomarkers. The three markers'model (CK-MB-HEPC-PLa2G2A) had the highest diagnostic accuracy at 82% (95% CI 56-82%) after cross-validation.
Conclusion: CK-MB and HEPC levels were statistically different between confirmed TB cases and non-TB cases. This study yields promising results for the rapid diagnosis of TB disease using a single marker or three biomarkers model.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Creatine kinase-MB; Diagnosis; Hepcidin; Tuberculosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO | Global tuberculosis report 2018 [Internet]. WHO. Available 2019 Aug 29, from http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/en/. Accessed 29 Aug 2019
-
- Perez-Velez CM, Marais BJ. Disease burden and recent epidemiologic shifts. Tuberculosis. 2012 doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1008049. - DOI
-
- Ngabonziza JCS, Ssengooba W, Mutua F, Torrea G, Dushime A, Gasana M, Andre E, Uwamungu S, Nyaruhirira AU, Mwaengo D, Muvunyi CM. Diagnostic performance of smear microscopy and incremental yield of Xpert in detection of pulmonary tuberculosis in Rwanda. BMC Infect Dis. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-2009-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chegou NN, Essone PN, Loxton AG, Stanley K, Black GF, van der Spuy GD, van Helden PD, Franken KL, Parida SK, Klein MR, Kaufmann SHE, Ottenhoff THM, Walzl G. Potential of host markers produced by infection phase-dependent antigen-stimulated cells for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in a highly endemic area. PLoS ONE. 2012 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038501. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

