Circulating Tumour DNA in Melanoma-Clinic Ready?
- PMID: 35133615
- PMCID: PMC8885536
- DOI: 10.1007/s11912-021-01151-6
Circulating Tumour DNA in Melanoma-Clinic Ready?
Abstract
Purpose of review: Liquid biopsies, including circulating tumour DNA (ctDNA), can inform a variety of clinical questions. This review examines the potential role of ctDNA as a clinical tool to inform clinical decision-making from early to late stage cutaneous melanoma.
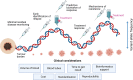
Recent findings: In pre-clinical studies, ctDNA has been shown to detect minimal residual disease and molecular relapse; predict and monitor response to therapy; and identify key resistance mechanisms. Here, we examine the potential utility of ctDNA and discuss its limitations for use in patients with melanoma. We present novel clinical trials, which are testing its value as a tool to augment clinical decision-making. Finally, we discuss the steps that are needed to ensure that ctDNA is used optimally in order to improve outcomes for patients with melanoma. Preclinical studies have shown that ctDNA has huge potential to provide real-time information about disease status in patients with melanoma. It is now time to test it rigorously within clinical trials to assess how it can be optimally used to benefit patients in the clinic.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Immunotherapy; Liquid biopsies; Melanoma; Targeted therapy; ctDNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Ann Tivey is supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) as an NIHR Academic Clinical Fellow.
Fiona Britton declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Julie-Ann Scott declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Dominic Rothwell declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Paul Lorigan has received clinical trial support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline and Amgen; has received speaker’s honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Laboratoires Pierre Fabre, NeraCare, Roche and Oncology Education Canada; and has received compensation for participation on advisory boards from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Novartis, GlaxoSmithKline, Amgen, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd, Laboratoires Pierre Fabre, NeraCare, Roche and Oncology Education Canada.
Rebecca Lee has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb for the CAcTUS Trial, and has received speaker’s honoraria from AstraZeneca.
Figures
References
-
- Schwarzenbach H, Hoon DSB, Pantel K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(6):426–437. - PubMed
-
- Sorenson G, Pribish D, Valone F, Memoli V, Bzik D, Yao S. Soluble normal and mutated DNA sequences from single-copy genes in human blood. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1994;3(1):67–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials