Outcomes of peritoneal dialysis in elderly vs non-elderly patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35134073
- PMCID: PMC8824377
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263534
Outcomes of peritoneal dialysis in elderly vs non-elderly patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Several studies have compared outcomes of peritoneal dialysis (PD) between elderly and non-elderly patients but with variable results. We hereby designed this review to compare mortality, peritonitis, and technique survival between elderly and non-elderly patients on PD.
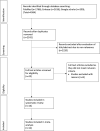
Methods: PubMed, Embase, and Google Scholar were searched for studies comparing outcomes of PD between elderly and non-elderly patients. The last search date was 14th July 2021.
Results: Fourteen studies were included. 12 studies defined the elderly as ≥65 years of age and these were included in the meta-analysis. Pooled analysis of crude (RR: 2.45 95% CI: 1.36, 4.40 I2 = 97% p = 0.003) and adjusted data (HR: 2.80 95% CI: 2.45, 3.09 I2 = 0% p<0.00001) indicated a statistically significant increased risk of mortality amongst elderly patients as compared to non-elderly patients. Meta-analysis of four studies demonstrated a statistically significant increased risk of peritonitis in the elderly (RR: 1.56 95% CI: 1.18, 2.07 I2 = 76% p = 0.002). Pooled analysis demonstrated no statistically significant difference in technique survival between the two groups (RR: 0.95 95% CI: 0.86, 1.05 I2 = 86% p = 0.32).
Conclusion: Elderly patients on PD have a significantly increased risk of mortality as compared to non-elderly patients. The risk of peritonitis is also significantly increased in older adults but the increased age has no impact on technique survival. Further studies are needed to strengthen our conclusions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


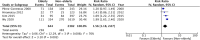

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

