Helicobacter pylori-induced RASAL2 Through Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB Promotes Gastric Tumorigenesis via β-catenin Signaling Axis
- PMID: 35134322
- PMCID: PMC9038683
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.01.046
Helicobacter pylori-induced RASAL2 Through Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB Promotes Gastric Tumorigenesis via β-catenin Signaling Axis
Abstract
Background & aims: Helicobacter pylori infection is the predominant risk factor for gastric cancer. RAS protein activator like 2 (RASAL2) is considered a double-edged sword in carcinogenesis. Herein, we investigated the role of RASAL2 in response to H pylori infection and gastric tumorigenesis.
Methods: Bioinformatics analyses of local and public databases were applied to analyze RASAL2 expression, signaling pathways, and clinical significance. In vitro cell culture, spheroids, patient-derived organoids, and in vivo mouse models were used. Molecular assays included chromatin immunoprecipitation, co-immunoprecipitation, Western blotting, quantitative polymerase chain reaction, and immunocyto/histochemistry.
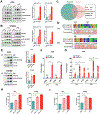
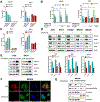
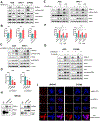
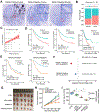
Results: H pylori infection induced RASAL2 expression via a nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent mechanism whereby NF-κB was directly bound to the RASAL2 promoter activating its transcription. By gene silencing and ectopic overexpression, we found that RASAL2 upregulated β-catenin transcriptional activity. RASAL2 inhibited protein phosphatase 2A activity through direct binding with subsequent activation of the AKT/β-catenin signaling axis. Functionally, RASAL2 silencing decreased nuclear β-catenin levels and impaired tumor spheroids and organoids formation. Furthermore, the depletion of RASAL2 impaired tumor growth in gastric tumor xenograft mouse models. Clinicopathological analysis indicated that abnormal overexpression of RASAL2 correlated with poor prognosis and chemoresistance in human gastric tumors.
Conclusions: These studies uncovered a novel signaling axis of NF-κB/RASAL2/β-catenin, providing a novel link between infection, inflammation and gastric tumorigenesis.
Keywords: Gastric Cancer; Helicobacter pylori; RASAL2; Tumorigenesis; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
How Can We Better Understand the Gastric Carcinogenesis of Helicobacter pylori?Gastroenterology. 2022 Oct;163(4):1121-1122. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.04.018. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 35469907 No abstract available.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Niwa T, Tsukamoto T, Toyoda T, et al. Inflammatory processes triggered by Helicobacter pylori infection cause aberrant DNA methylation in gastric epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2010;70:1430–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

