DALY Estimation Approaches: Understanding and Using the Incidence-based Approach and the Prevalence-based Approach
- PMID: 35135044
- PMCID: PMC8841194
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.21.597
DALY Estimation Approaches: Understanding and Using the Incidence-based Approach and the Prevalence-based Approach
Abstract
Disability-adjusted life-year (DALY) estimates may vary according to factors such as the standard life expectancy, age weighting, time preference and discount rate, calculation of disability weights, and selection of the estimation method. DALY estimation methods are divided into the following 3 approaches: the incidence-based approach, the pure prevalence-based approach, and the hybrid approach. These 3 DALY estimation approaches each reflect different perspectives on the burden of disease using unique characteristics, based on which the selection of a suitable approach may vary by the purpose of the study. The Global Burden of Disease studies, which previously estimated DALYs using the incidence-based approach, switched to using the hybrid approach in 2010, while the National Burden of Disease studies in Korea still mainly apply the incidence-based approach. In order to increase comparability with other international burden of disease studies, more DALY studies using the prevalence-based approach need to be conducted in Korea. However, with the limitations of the hybrid approach in mind, it is necessary to conduct more research using a disease classification system suitable for Korea. Furthermore, more detailed and valid data sources should be established before conducting studies using a broader variety of DALY estimation approaches. This review study will help researchers on burden of disease use an appropriate DALY estimation approach and will contribute to enhancing researchers' ability to critically interpret burden of disease studies.
Keywords: Disability weight; Disability-adjusted life-year; Incidence; Prevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
Figures

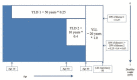

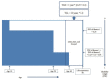

Similar articles
-
Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Lancet Psychiatry. 2022 Feb;9(2):137-150. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35026139 Free PMC article.
-
Nations within a nation: variations in epidemiological transition across the states of India, 1990-2016 in the Global Burden of Disease Study.Lancet. 2017 Dec 2;390(10111):2437-2460. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32804-0. Epub 2017 Nov 14. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 29150201 Free PMC article.
-
Global, regional and national burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2019.BMJ Glob Health. 2021 Nov;6(11):e004128. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-004128. BMJ Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 34844997 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring the Burden of Disease Due to Preterm Birth Complications in Korea Using Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALY).Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Feb 12;16(3):519. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16030519. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 30759822 Free PMC article.
-
Methodological choices in brucellosis burden of disease assessments: A systematic review.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Dec 13;16(12):e0010468. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010468. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 36512611 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Estimating the impact of a police education program on hepatitis C virus transmission and disease burden among people who inject drugs in Tijuana, Mexico: A dynamic modeling analysis.Addiction. 2023 Sep;118(9):1763-1774. doi: 10.1111/add.16203. Epub 2023 May 1. Addiction. 2023. PMID: 37039246 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of alcohol use disorder and its consequences in Iran from 1990 to 2019: Findings from the global burden of disease study.Prev Med Rep. 2024 Aug 20;46:102872. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2024.102872. eCollection 2024 Oct. Prev Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39253724 Free PMC article.
-
Korean National Burden of Disease: The Importance of Diabetes Management.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Jul;48(4):518-530. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0087. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39091003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Neuroaging on Earth and in Spaceflight.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 18;26(4):1738. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041738. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The disease burden of bladder cancer and its attributable risk factors in five Eastern Asian countries, 1990-2019: a population-based comparative study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 4;24(1):2404. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-19909-5. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39232688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Bank . World development report 1993: investing in health. 16th ed. New York: Oxford University Press; 1993. pp. 1–16.
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Regional patterns of disability-free life expectancy and disability-adjusted life expectancy: global burden of disease study. Lancet. 1997;349(9062):1347–1352. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Global mortality, disability, and the contribution of risk factors: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 1997;349(9063):1436–1442. - PubMed
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990-2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 1997;349(9064):1498–1504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

