Detoxification vs non-detoxification before starting an anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody in medication overuse headache
- PMID: 35135357
- PMCID: PMC9109244
- DOI: 10.1177/03331024211067791
Detoxification vs non-detoxification before starting an anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody in medication overuse headache
Abstract
Background: Medication overuse headache significantly contributes to the chronification process and treatment refractoriness of migraine. Currently, abrupt discontinuation of the overused medication still represents the best management strategy for these patients, challenging public health system resources.
Methods: In this prospective study, chronic migraine and medication overuse headache sufferers with at least 28 days of analgesic consumption per month were included. Assessment of efficacy outcomes at three months were compared among patients who underwent in-hospital abrupt discontinuation of overused acute medication (YES-DETOX group) and patients who did not (NO-DETOX group) before starting an anti-CGRP monoclonal antibody.
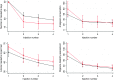
Results: Of 401 patients who received either erenumab or galcanezumab, 28% (n = 111) satisfied inclusion criteria (YES-DETOX n = 28; NO-DETOX n = 83). After three months of treatment, 59% (n = 65; 47/83 YES-DETOX; 18/28 NO-DETOX) patients reverted from medication overuse headache and 51% (n = 57; 42/83 YES-DETOX; 15/28 NO-DEOTX) achieved ≥50% reduction in monthly headache days; yet no statistical differences were observed between the two groups (p = 0.4788 and p = 0.8393, respectively). Monthly consumption of pain medication was the only baseline prognostic factor in multivariate analysis in the overall cohort (p = 0.016).
Conclusion: Our results support the emerging evidence that anti-CGRP monoclonal antibodies may be effective in medication overuse headache patients irrespective of detoxification, yet further studies are needed to draw definitive conclusions.
Keywords: Refractory migraine; calcitonin gene-related peptide; chronic migraine; drugs withdrawal; erenumab; galcanezumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS) The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018; 38: 1–211. - PubMed
-
- Diener HC, Holle D, Solbach K, et al.. Medication-overuse headache: risk factors, pathophysiology and management. Nat Rev Neurol 2016; 12: 575–83. - PubMed
-
- Colas R, Munoz P, Temprano R, et al.. Chronic daily headache with analgesic overuse: epidemiology and impact on quality of life. Neurology 2004; 62: 1338–1342. - PubMed
-
- Diener HC, Antonaci F, Braschinsky M, et al.. European Academy of Neurology guideline on the management of medication-overuse headache. Eur J Neurol 2020; 27: 1102–1116. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

