Evaluation of lateral pterygoid muscle in patients with temporomandibular joint anterior disk displacement using T1-weighted Dixon sequence: a retrospective study
- PMID: 35135518
- PMCID: PMC8826701
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-022-05079-1
Evaluation of lateral pterygoid muscle in patients with temporomandibular joint anterior disk displacement using T1-weighted Dixon sequence: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Pathological alterations of lateral pterygoid muscle (LPM) are implicated in temporomandibular joint anterior disk displacement (ADD). However, quantification of the fatty infiltration of LPM and its correlation with ADD have rarely been reported. The aim of this study was to evaluate the fatty infiltration, morphological features and texture features of LPM in patients with ADD using T1-weighted Dixon sequence.
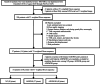
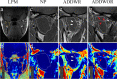
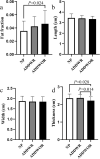
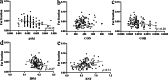
Methods: This retrospective study included patients who underwent temporomandibular joint MRI with T1-weighted Dixon sequence between December 2018 and August 2020. The temporomandibular joints of the included patients were divided into three groups according to the position of disk: Normal position disk (NP) group, Anterior disk displacement with reduction (ADDWR) group and Anterior disk displacement without reduction (ADDWOR) group. Fat fraction, morphological features (Length; Width; Thickness), and texture features (Angular second moment; Contrast; Correlation; Inverse different moment; Entropy) extracted from in-phase image of LPM were evaluated. One-way ANOVA, Welch's ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test, Spearman and Pearson correlation analysis were performed. Intra-class correlation coefficient was used to evaluate the reproducibility.
Results: A total of 53 patients with 106 temporomandibular joints were evaluated. Anterior disk displacement without reduction group showed higher fat fraction than normal position disk group (P = 0.024). Length of LPM was negatively correlated with fat fraction (r = -0.22, P = 0.026). Angular second moment (ρ = -0.32, P < 0.001), correlation (ρ = -0.28, P = 0.003) and inverse different moment (ρ = -0.27, P = 0.005) were negatively correlated with fat fraction, while positive correlation was found between entropy and fat fraction (ρ = 0.31, P = 0.001). The intra-class correlation coefficients for all values were ranged from 0.80 to 0.97.
Conclusions: Patients with ADDWOR present more fatty infiltration in the LPM compared to NP or ADDWR patients. Fatty infiltration of LPM was associated with more atrophic and higher intramuscular heterogeneity in patients with ADD. Fat fraction of LPM quantitatively and noninvasively evaluated by Dixon sequence may has utility as an imaging-based marker of the structural severity of ADD disease process, which could be clinical helpful for the early diagnose of ADD and predication of disease progression.
Keywords: Anterior disk displacement; Dixon sequence; Fatty infiltration; Lateral pterygoid muscle; Texture analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Quantitative MRI texture analysis of the lateral pterygoid muscle in unilateral temporomandibular joint disorders.Head Face Med. 2025 Apr 28;21(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13005-025-00512-x. Head Face Med. 2025. PMID: 40296140 Free PMC article.
-
Gender differences in lateral pterygoid muscle in patients with anterior disk displacement.Oral Dis. 2023 Nov;29(8):3481-3492. doi: 10.1111/odi.14391. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Oral Dis. 2023. PMID: 36152024
-
Clinical study of magnetic resonance imaging-based texture analysis and fasciculation of the lateral pterygoid muscle in young patients with temporomandibular disorder.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2023 Sep;136(3):382-393. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2023.05.002. Epub 2023 May 10. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37357069
-
Etiopathogenesis of disk displacement of the temporomandibular joint: a review of the mechanisms.Indian J Dent Res. 2009 Apr-Jun;20(2):212-21. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.51365. Indian J Dent Res. 2009. PMID: 19553725 Review.
-
Imaging features of chondrosarcoma of the temporomandibular joint: report of nine cases and literature review.Clin Radiol. 2020 Nov;75(11):878.e1-878.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2020.07.016. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Clin Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32843140 Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative MRI texture analysis of the lateral pterygoid muscle in unilateral temporomandibular joint disorders.Head Face Med. 2025 Apr 28;21(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s13005-025-00512-x. Head Face Med. 2025. PMID: 40296140 Free PMC article.
-
The T1 mapping and T2 mapping of lateral pterygoid muscle: a quantitative analysis in patients with acute and chronic temporomandibular joint disorders.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul 11. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11795-8. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40646340
-
Three-dimensional digital anatomical measurements of pterygoid plates and posterior maxillary region.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):1494. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05176-8. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39696184 Free PMC article.
-
Relation between Condyle Horizontal Angle and Intercondylar Angle with Disc Displacement in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Disorders: An MRI Evaluation.Radiol Res Pract. 2023 Sep 8;2023:3846525. doi: 10.1155/2023/3846525. eCollection 2023. Radiol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37719870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luder HU, Bobst P. Wall architecture and disc attachment of the human temporomandibular joint. Schweiz Monatsschr Zahnmed. 1991;101(5):557–570. - PubMed
-
- Ngamsom S, Nakamura S, Sakamoto J, Kotaki S, Tetsumura A, Kurabayashi T. The intravoxel incoherent motion MRI of lateral pterygoid muscle: a quantitative analysis in patients with temporomandibular joint disorders. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2017;46(5):20160424. doi: 10.1259/dmfr.20160424. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

