Functional network topography of the medial entorhinal cortex
- PMID: 35135885
- PMCID: PMC8851479
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2121655119
Functional network topography of the medial entorhinal cortex
Abstract
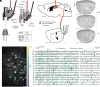
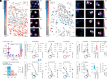
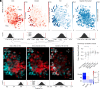
The medial entorhinal cortex (MEC) creates a map of local space, based on the firing patterns of grid, head-direction (HD), border, and object-vector (OV) cells. How these cell types are organized anatomically is debated. In-depth analysis of this question requires collection of precise anatomical and activity data across large populations of neurons during unrestrained behavior, which neither electrophysiological nor previous imaging methods fully afford. Here, we examined the topographic arrangement of spatially modulated neurons in the superficial layers of MEC and adjacent parasubiculum using miniaturized, portable two-photon microscopes, which allow mice to roam freely in open fields. Grid cells exhibited low levels of co-occurrence with OV cells and clustered anatomically, while border, HD, and OV cells tended to intermingle. These data suggest that grid cell networks might be largely distinct from those of border, HD, and OV cells and that grid cells exhibit strong coupling among themselves but weaker links to other cell types.
Keywords: entorhinal cortex; grid cells; spatial coding; topography; two-photon microscopy.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Penfield W., Rasmussen T., The Cerebral Cortex of Man: A Clinical Study of Localization of Function (Macmillan, 1950).
-
- Udin S. B., Fawcett J. W., Formation of topographic maps. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 289–327 (1988). - PubMed
-
- Hubel D. H., Wiesel T. N., Receptive fields and functional architecture in two nonstriate visual areas (18 and 19) of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 229–289 (1965). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

